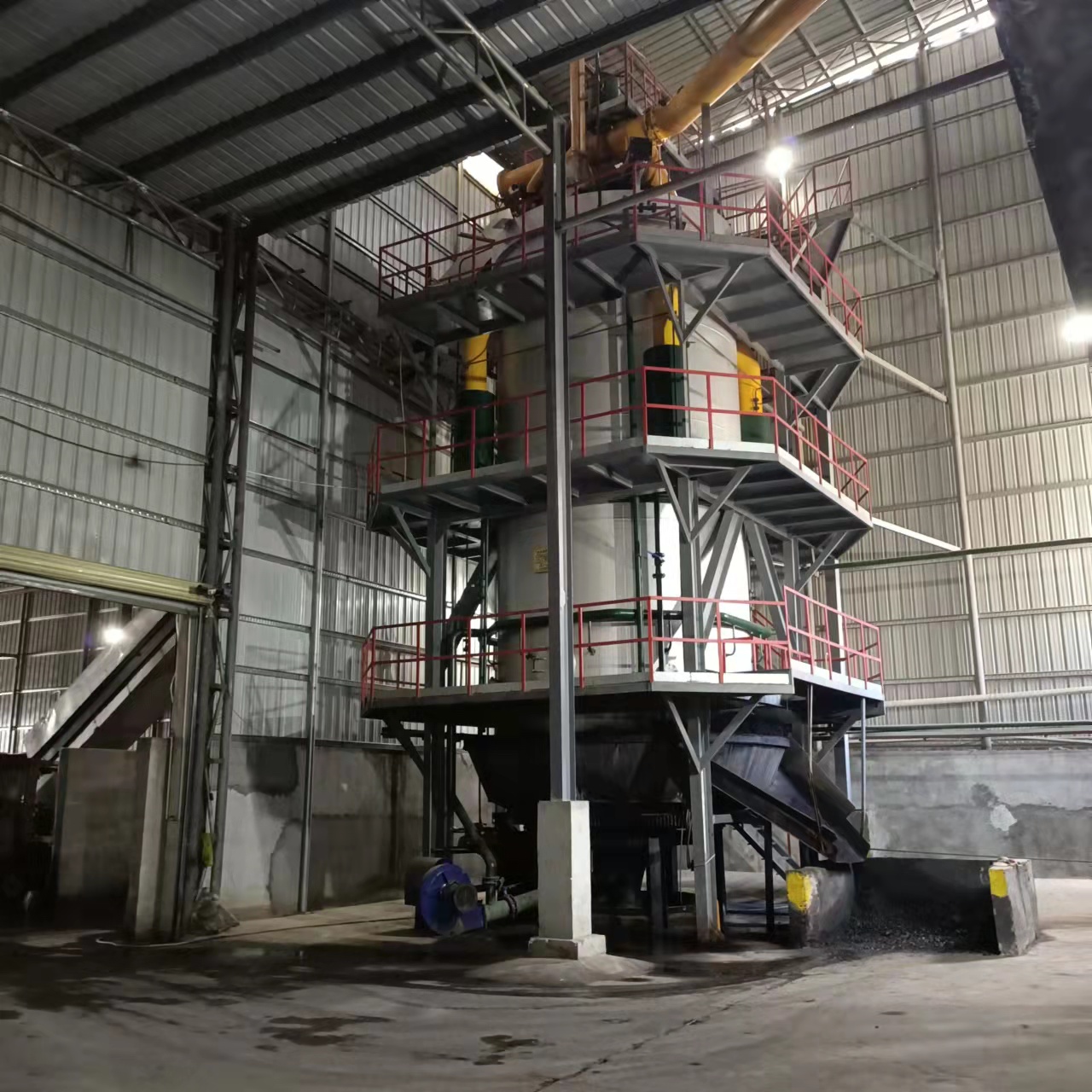
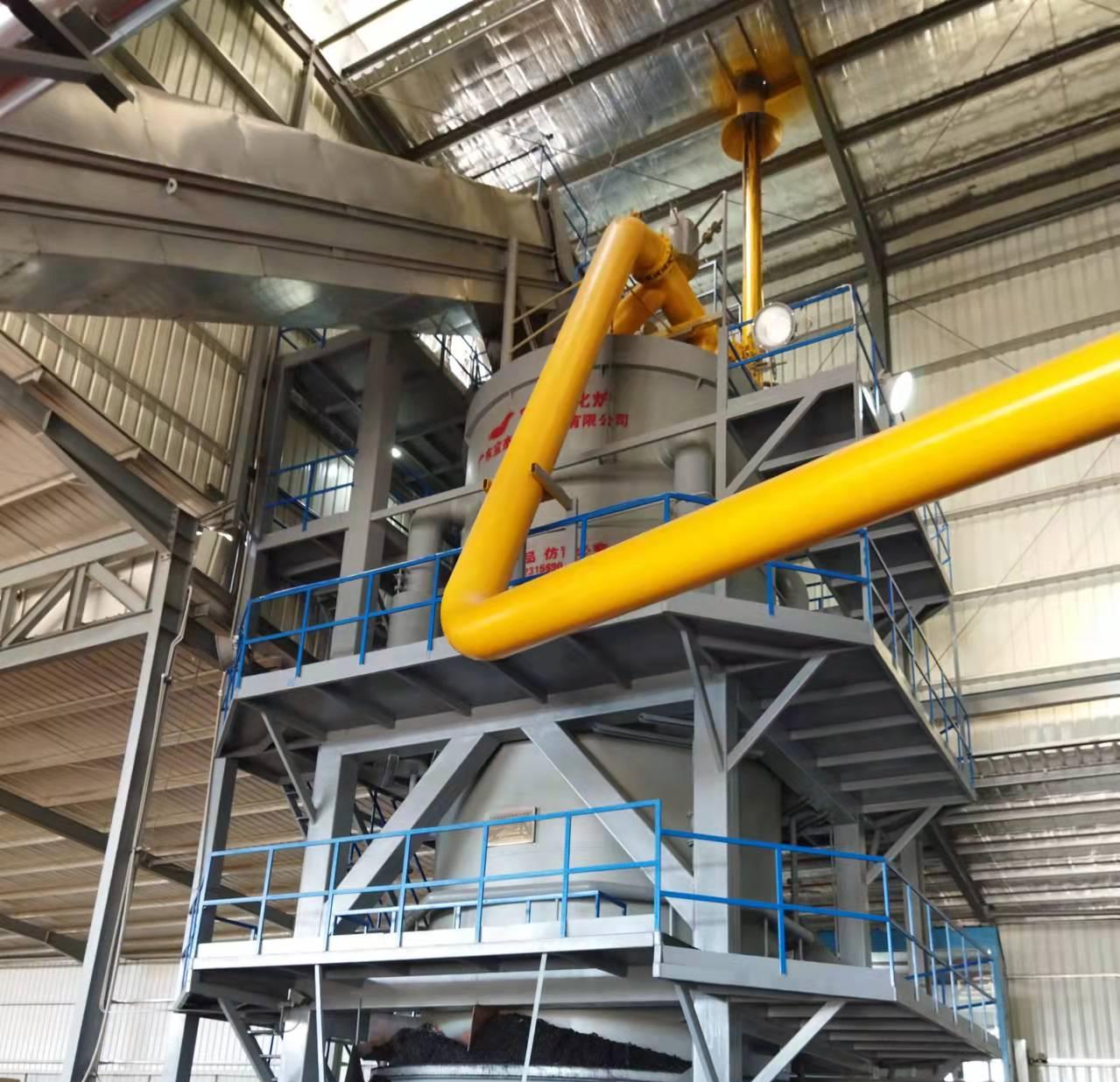
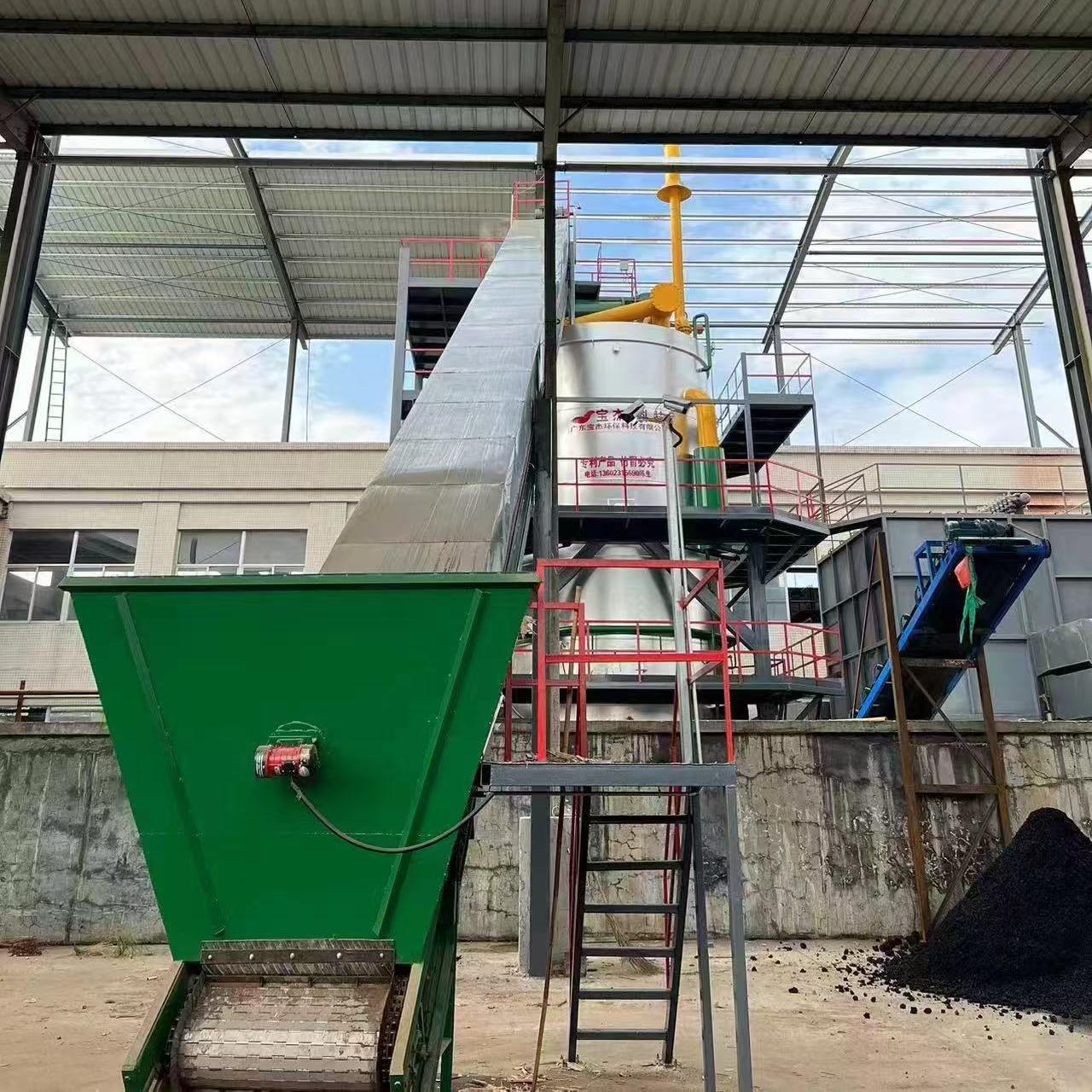
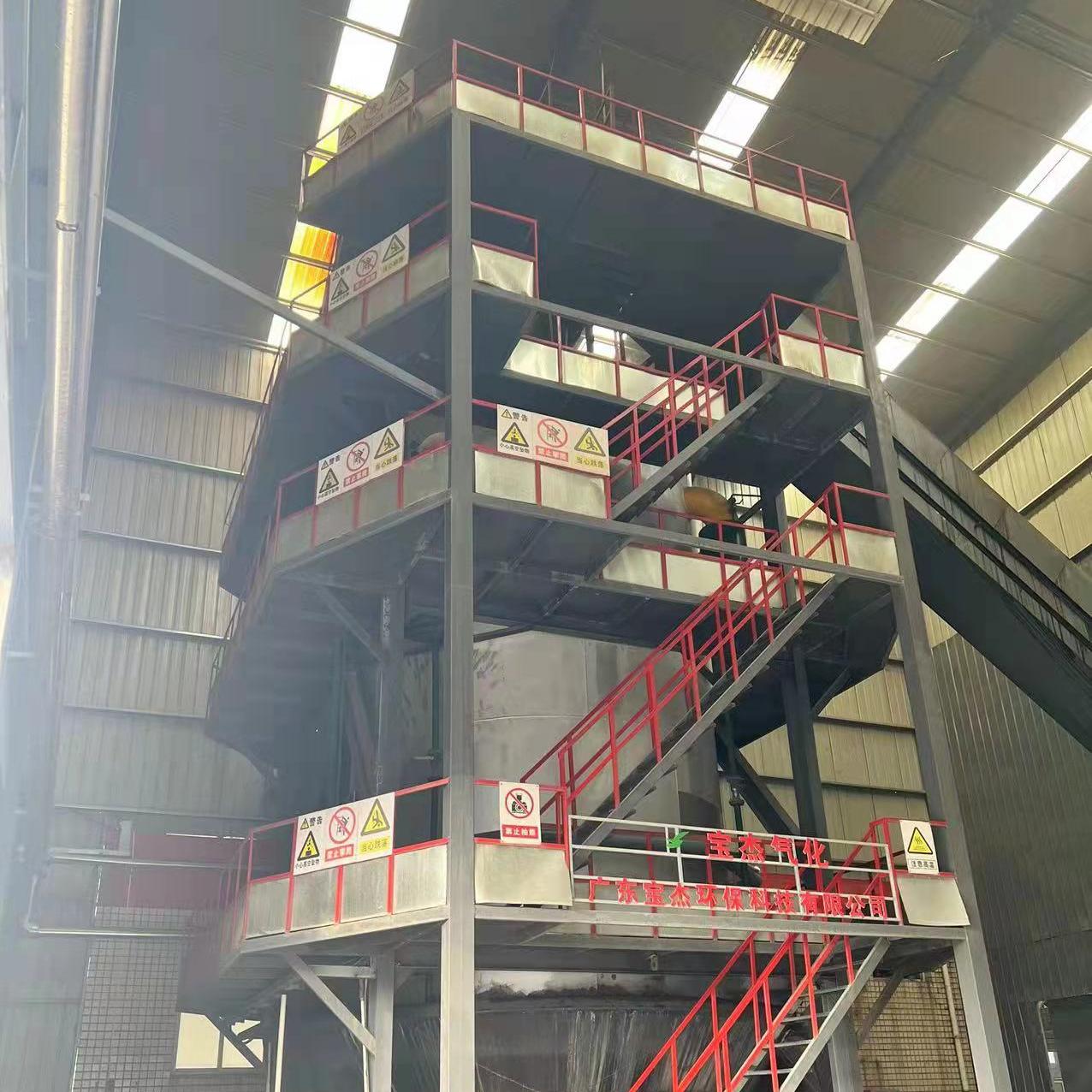
R&D and manufacture of biomass gasification equipment, environmental protection equipment, boiler equipment, investment in heating (steam) energy operation and management.
Tel:+86 0769-82928980
E-mail:[email protected]
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Industry News
Why Is a Biomass Gas Boiler Becoming the Smart Choice for Clean Energy Heating?
In recent years, the shift towards clean and renewable energy has accelerated, and biomass gas boilers have emerged as one of the most promising solutions in sustainable heating technology. They combine the benefits of renewable fuel sources with advanced gasification technology to deliver high efficiency, low emissions, and long-term cost savings. But what exactly is a biomass gas boiler, how does it work, and why is it considered an eco-friendly heating option?
1. What Is a Biomass Gas Boiler?
A biomass gas boiler is a heating system that uses biomass—such as wood pellets, agricultural residues, or forestry waste—as fuel. Instead of directly burning the biomass like traditional biomass boilers, it gasifies the biomass to produce a combustible gas known as syngas (synthetic gas). This syngas is then burned in the boiler’s combustion chamber to produce heat for industrial processes, commercial buildings, or district heating systems.
This process ensures more complete combustion, higher efficiency, and fewer harmful emissions compared to traditional solid-fuel boilers.

2. How Does a Biomass Gas Boiler Work?
The working principle of a biomass gas boiler involves three main stages:
-
Gasification Process
- Biomass is heated in a low-oxygen environment, which causes it to release volatile gases without fully combusting.
- These gases (mainly carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and methane) form syngas.
-
Gas Cleaning
- The syngas is filtered and cooled to remove tar, ash, and particulates, ensuring cleaner combustion.
-
Gas Combustion
- The purified syngas is fed into the boiler’s burner system, where it burns at high temperatures to produce thermal energy.
This process improves efficiency and reduces the environmental footprint.
3. Advantages of a Biomass Gas Boiler
a. Environmental Benefits
- Carbon Neutral: Biomass fuel releases only the amount of CO₂ absorbed during its growth cycle, making it nearly carbon-neutral.
- Lower Emissions: Advanced gasification significantly reduces particulate matter and NOx emissions compared to coal or oil boilers.
b. Cost Savings
- Cheaper Fuel: Biomass sources like wood chips or agricultural waste are often less expensive than fossil fuels.
- Energy Independence: Reduces reliance on imported fuels, stabilizing energy costs.
c. High Efficiency
- Efficiency rates can reach 85–95% due to complete combustion of syngas.
- Lower fuel consumption compared to traditional biomass boilers.
d. Fuel Flexibility
- Can use a variety of biomass feedstocks, from forestry waste to crop residues.
4. Common Applications
Biomass gas boilers are used in:
- Industrial heating (food processing, textile manufacturing, paper mills)
- Commercial buildings (hospitals, hotels, schools)
- District heating systems for residential communities
- Agricultural facilities (greenhouses, grain drying)
5. Challenges and Considerations
Despite their benefits, biomass gas boilers require:
- Consistent fuel quality for stable performance.
- Initial high investment costs compared to conventional boilers.
- Space for biomass storage and handling systems.
- Regular maintenance to ensure optimal efficiency.
6. Comparison Table: Biomass Gas Boiler vs. Traditional Fossil Fuel Boiler
| Feature / Factor | Biomass Gas Boiler | Fossil Fuel Boiler |
| Fuel Source | Renewable biomass (wood chips, pellets, waste) | Non-renewable (coal, oil, natural gas) |
| Carbon Emissions | Near carbon-neutral | High CO₂ emissions |
| Efficiency | 85–95% | 70–90% |
| Fuel Cost | Lower (especially in rural areas) | Higher and volatile |
| Air Pollution | Low particulates & NOx | High particulates & NOx |
| Operational Cost | Moderate (maintenance required) | Moderate to high |
| Installation Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower initial investment |
| Energy Security | High (local fuel supply possible) | Low (depends on imports) |
7. Future Outlook
With governments worldwide pushing for decarbonization, biomass gas boilers are likely to become a more common heating solution. Technological improvements in gasification and automated fuel handling systems will further increase their efficiency and reduce operational complexity.
In addition, carbon credit systems and renewable energy subsidies can shorten the payback period for biomass gas boiler investments, making them attractive to both industries and commercial facilities.
Conclusion
A biomass gas boiler represents a smart, sustainable, and economically viable heating solution for those looking to reduce their carbon footprint without compromising on performance. While it requires a higher initial investment and careful fuel management, the long-term savings, environmental benefits, and efficiency gains make it a future-ready choice for both industrial and commercial applications.
Quick Links
Products
contact Us
 Tel: +86 0769-82928980
Tel: +86 0769-82928980 Fax: [email protected]
Fax: [email protected] E-mail: [email protected]
E-mail: [email protected] Company Address: Dalang Chamber of Commerce Building, No. 288 Yinlang South Road, Dalang Town, Dongguan City 13333, China
Company Address: Dalang Chamber of Commerce Building, No. 288 Yinlang South Road, Dalang Town, Dongguan City 13333, China Factory Add:
West side of Centre Road and south side of Zhongyuan Road within Hongcaoyuan, Hongcao Town, Shanwei Urban District
Factory Add:
West side of Centre Road and south side of Zhongyuan Road within Hongcaoyuan, Hongcao Town, Shanwei Urban District
Copyright© 2022 Guangdong Bao Jie Technology Co., Ltd.All Rights Reserved.


 EN
EN 





