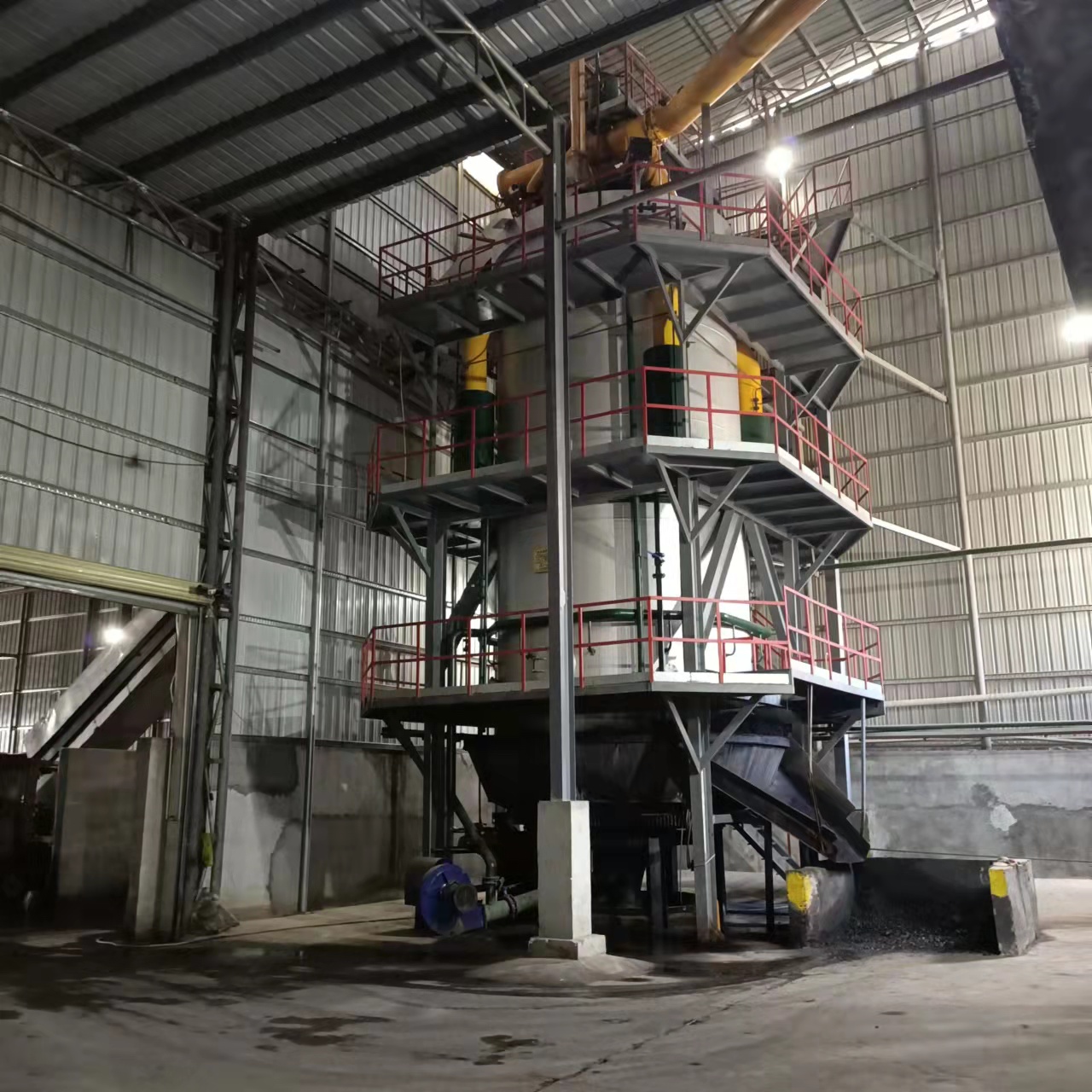
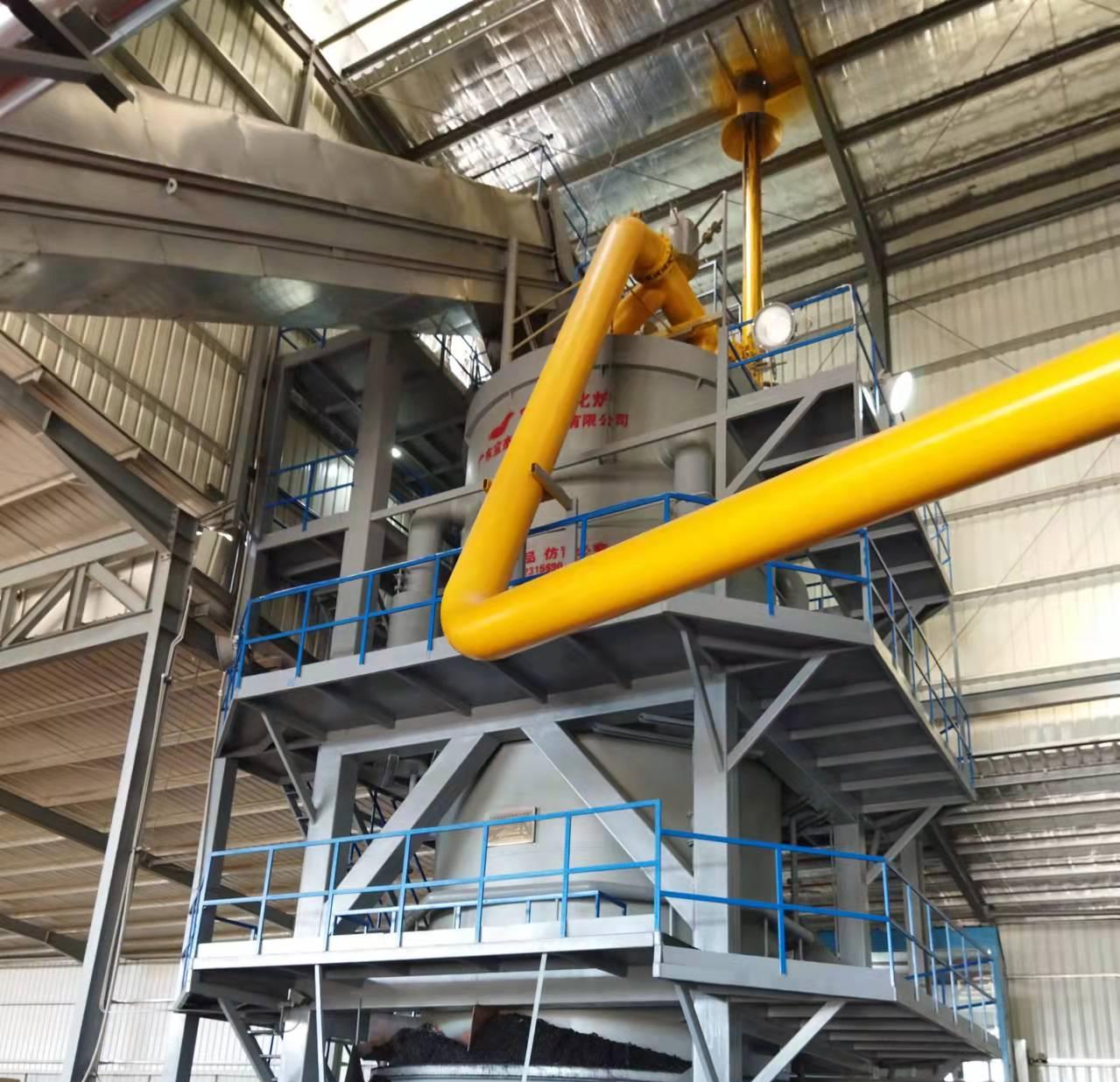
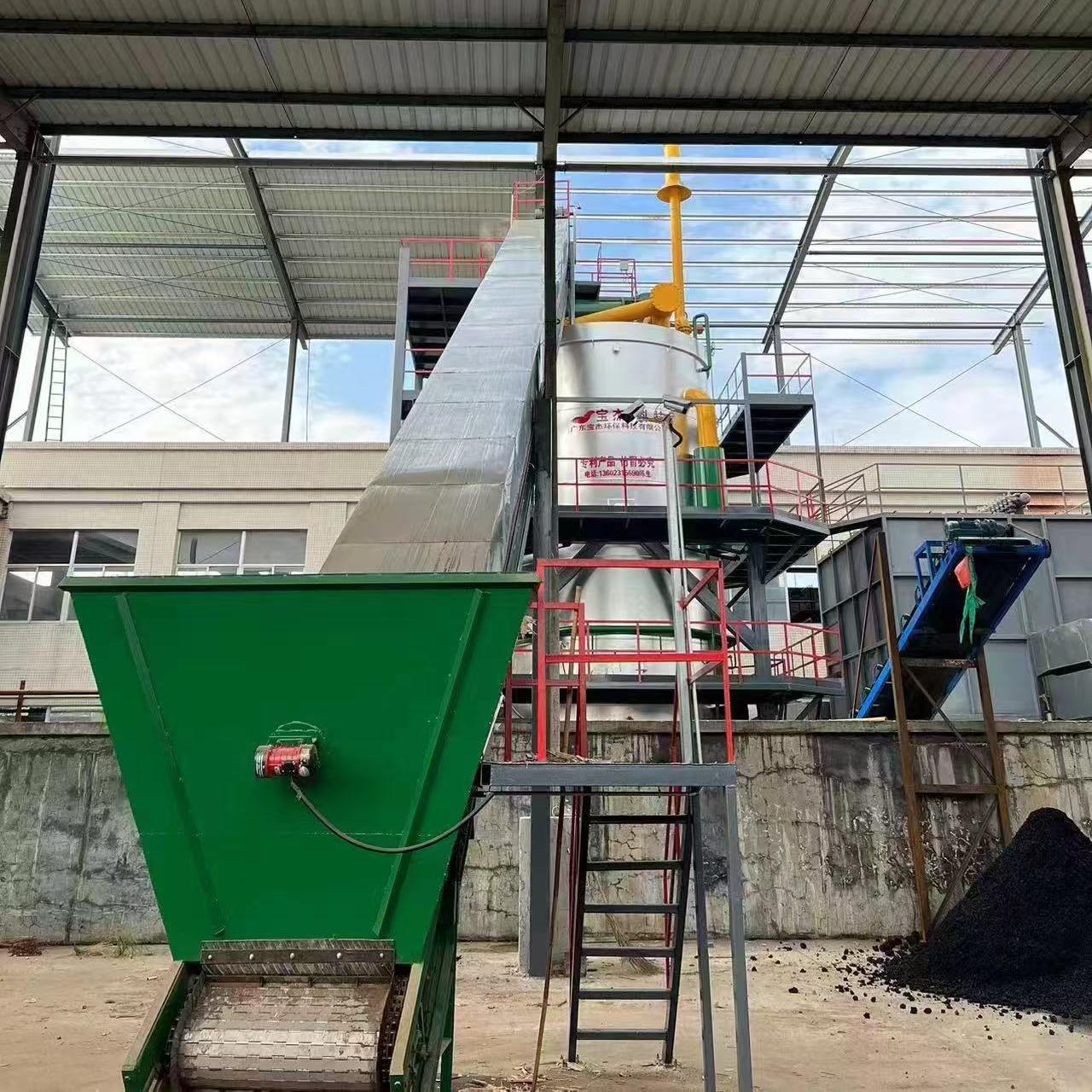
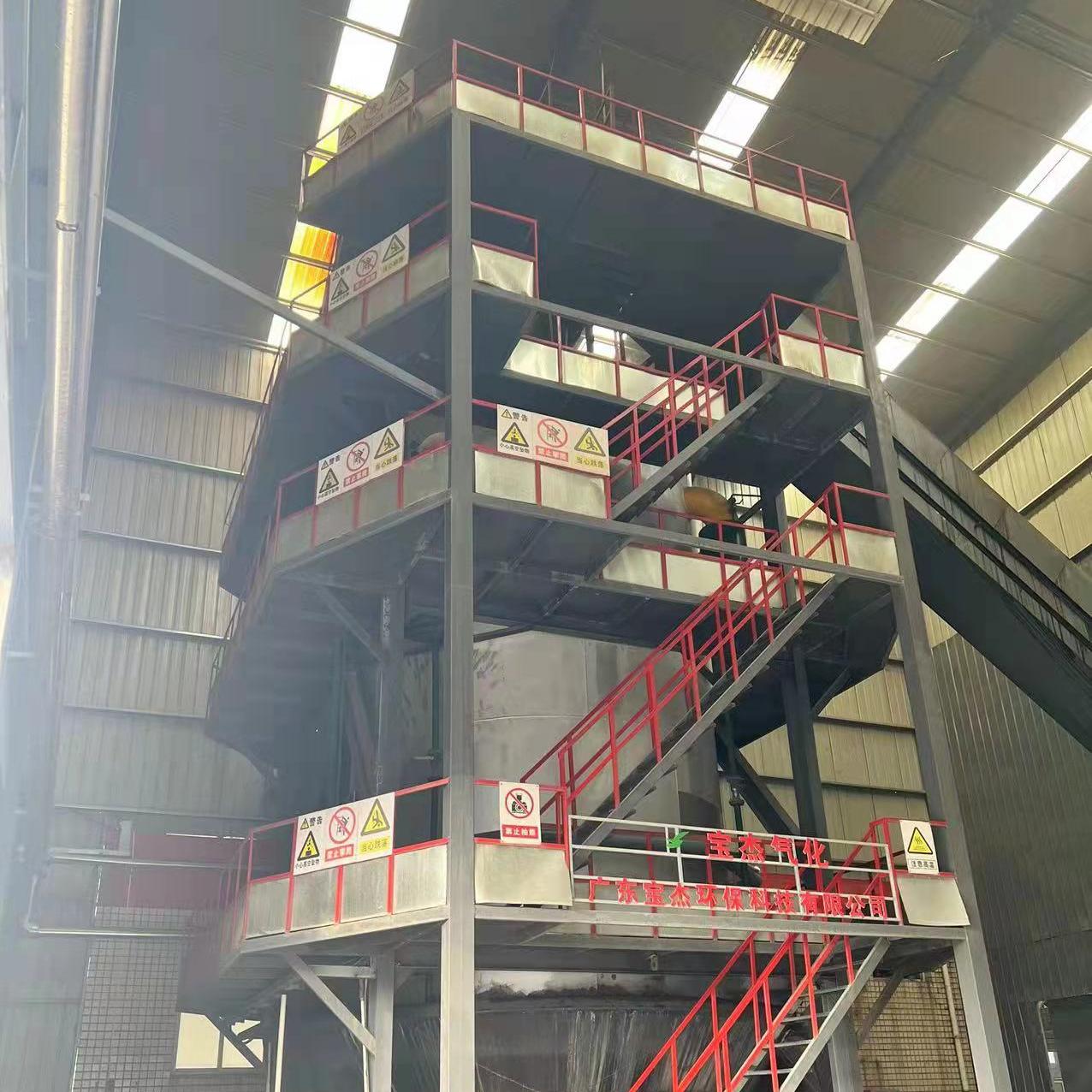
R&D and manufacture of biomass gasification equipment, environmental protection equipment, boiler equipment, investment in heating (steam) energy operation and management.
Tel:+86 0769-82928980
E-mail:[email protected]
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Industry News
Biomass Gas Boiler: The Sustainable Heating Solution for a Greener Future
As the world shifts toward cleaner energy and reduced carbon emissions, industries, commercial facilities, and residential users are seeking eco-friendly alternatives to traditional fossil fuel-based heating systems. Among the most promising and rapidly growing technologies is the Biomass Gas Boiler—a high-efficiency, renewable energy system that converts organic biomass materials into clean-burning gas to produce heat and hot water.
Combining the principles of gasification and combustion, biomass gas boilers offer a sustainable, cost-effective, and reliable alternative to coal, oil, or natural gas boilers. Whether you're operating a factory, greenhouse, school, or large-scale heating plant, a biomass gas boiler can significantly reduce your carbon footprint while lowering long-term energy costs.
In this comprehensive SEO-optimized article, we’ll explore what a biomass gas boiler is, how it works, its key benefits, applications, and why it’s becoming a cornerstone of modern green energy solutions.
What Is a Biomass Gas Boiler?
A biomass gas boiler is an advanced heating system that uses gasification technology to convert solid biomass fuels—such as wood chips, agricultural residues, rice husks, sawdust, or pellets—into combustible syngas (synthesis gas), which is then burned to generate heat. Unlike traditional biomass boilers that directly combust solid fuel, gas boilers first transform the biomass into a gaseous fuel, resulting in cleaner combustion, higher efficiency, and lower emissions.
This two-stage process—gasification followed by clean combustion—makes biomass gas boilers one of the most efficient and environmentally friendly heating technologies available today.
How Does a Biomass Gas Boiler Work?
The operation of a biomass gas boiler involves several key stages:
Fuel Feeding: Dried biomass (typically 10–30% moisture content) is automatically fed into the gasifier chamber.
Gasification: In a low-oxygen environment, the biomass is heated to high temperatures (700–900°C), breaking it down into syngas—a mixture of carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H₂), methane (CH₄), and other combustible gases.
Gas Cleaning: The raw syngas passes through a filtration system to remove tar, ash, and particulates, ensuring clean combustion.
Combustion: The purified gas is burned in a secondary combustion chamber with precise air control, producing high-temperature heat.
Heat Exchange: The heat is transferred to water or thermal oil, generating hot water, steam, or space heating.
Emission Control: Flue gases are treated through cyclones, bag filters, or scrubbers to meet environmental standards before release.
This advanced process ensures over 85% thermal efficiency and emissions that are significantly lower than those of conventional coal or oil boilers.
Key Benefits of Biomass Gas Boilers
| Benefit | Description |
| Renewable Energy Source | Uses organic waste materials that are naturally replenished. |
| Low Carbon Emissions | Carbon-neutral cycle—CO₂ released is offset by CO₂ absorbed during plant growth. |
| High Efficiency | Gasification + clean combustion delivers superior heat output. |
| Cost-Effective Fuel | Biomass is often cheaper and more stable in price than fossil fuels. |
| Waste Utilization | Converts agricultural, forestry, and industrial waste into energy. |
| Energy Independence | Reduces reliance on imported oil and gas. |
| Low Operating Costs | Automated systems reduce labor and maintenance needs. |
| Compliance with Green Regulations | Meets strict environmental standards in EU, USA, and Asia. |
These advantages make biomass gas boilers an ideal choice for businesses aiming to meet sustainability goals and reduce energy expenses.
Types of Biomass Gas Boilers
Biomass gas boilers are available in various configurations to suit different needs:
Fixed-Bed Gasifiers (Updraft/Down-draft): Simple design, ideal for small to medium-scale applications.
Fluidized Bed Gasifiers: Higher efficiency and better tar reduction—suitable for industrial use.
Dual-Chamber Boilers: Separate gasification and combustion chambers for cleaner burning.
Modular Systems: Scalable units that can be combined for higher capacity.
Power outputs range from 100 kW for small facilities to 10 MW or more for large industrial plants.
Common Biomass Fuels Used
Biomass gas boilers can run on a wide variety of organic materials, including:
Wood chips and sawdust
Rice husks and straw
Coconut shells
Corn cobs and stalks
Olive pits
Energy crops (e.g., miscanthus, switchgrass)
Compressed biomass pellets
The fuel should be dry (moisture < 30%) and uniformly sized to ensure stable gasification and efficient combustion.

Applications of Biomass Gas Boilers
1. Industrial Heating
Used in food processing, textile mills, paper factories, and chemical plants for steam and process heat.
2. District Heating Systems
Supplies centralized heating to residential complexes, hospitals, and schools in rural or urban areas.
3. Greenhouses and Agriculture
Provides consistent heat for crop cultivation, especially in cold climates.
4. Commercial Buildings
Hotels, spas, and swimming pools use biomass gas boilers for hot water and space heating.
5. Power Generation
When integrated with engines or turbines, syngas can generate electricity in combined heat and power (CHP) systems.
6. Off-Grid and Rural Energy
Ideal for remote communities without access to natural gas or electricity grids.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
One of the greatest advantages of biomass gas boilers is their positive environmental impact:
Carbon Neutrality: The CO₂ released during combustion is reabsorbed by new plant growth, creating a closed carbon cycle.
Waste Reduction: Utilizes agricultural and forestry residues that might otherwise be burned openly or left to decompose.
Lower Emissions: Produces significantly less SOx, NOx, and particulate matter than coal-fired boilers.
Renewable Resource: Biomass is abundant and can be sustainably harvested.
When paired with emission control systems, modern biomass gas boilers comply with EU BREF, U.S. EPA, and China GB standards, making them eligible for green energy incentives and carbon credits.
Economic Advantages
While the initial investment in a biomass gas boiler may be higher than a conventional boiler, the long-term savings are substantial:
Fuel Cost Savings: Biomass is often 30–50% cheaper than natural gas or diesel.
Government Incentives: Many countries offer subsidies, tax breaks, or feed-in tariffs for renewable energy projects.
Stable Pricing: Unlike fossil fuels, biomass prices are less volatile and locally sourced.
Reduced Carbon Taxes: Companies can avoid or reduce carbon levies by switching to renewable heating.
The payback period for a biomass gas boiler typically ranges from 3 to 7 years, depending on usage and fuel availability.
Maintenance and Operational Efficiency
Modern biomass gas boilers are designed for automated, low-maintenance operation:
Automatic fuel feeding and ash removal
Remote monitoring via IoT systems
Self-cleaning gasifiers and filters
Annual maintenance checks recommended
With proper care, these systems can operate reliably for 15–20 years or more.
Choosing the Right Biomass Gas Boiler
When selecting a system, consider:
Heating demand (kW or steam output required)
Available biomass fuel type and supply
Space and installation requirements
Emission standards in your region
Automation and control features
After-sales service and warranty
Always choose a certified manufacturer with proven installations and compliance with international standards (CE, ISO, ASME).
The Future of Biomass Gas Boilers
As global decarbonization efforts accelerate, biomass gasification technology is evolving rapidly:
Hybrid Systems: Integration with solar or biogas for multi-source energy.
Smart Boilers: AI-powered optimization for fuel use and emissions.
Tar-Free Gasification: Advanced catalytic processes reduce tar formation.
Small-Scale Domestic Units: Compact designs for homes and small businesses.
With ongoing innovation, biomass gas boilers are set to play a key role in the transition to a circular, low-carbon economy.
Conclusion
The biomass gas boiler is not just a heating system—it’s a sustainable energy solution that transforms waste into clean, reliable heat. By harnessing the power of nature’s most abundant resource—organic biomass—this technology offers a practical path toward energy independence, cost savings, and environmental responsibility.
From industrial plants to rural communities, biomass gas boilers are proving that green energy can be both powerful and profitable. As governments and businesses commit to net-zero goals, now is the perfect time to invest in this clean, renewable heating technology.
Quick Links
Products
contact Us
 Tel: +86 0769-82928980
Tel: +86 0769-82928980 Fax: [email protected]
Fax: [email protected] E-mail: [email protected]
E-mail: [email protected] Company Address: Dalang Chamber of Commerce Building, No. 288 Yinlang South Road, Dalang Town, Dongguan City 13333, China
Company Address: Dalang Chamber of Commerce Building, No. 288 Yinlang South Road, Dalang Town, Dongguan City 13333, China Factory Add:
West side of Centre Road and south side of Zhongyuan Road within Hongcaoyuan, Hongcao Town, Shanwei Urban District
Factory Add:
West side of Centre Road and south side of Zhongyuan Road within Hongcaoyuan, Hongcao Town, Shanwei Urban District
Copyright© 2022 Guangdong Bao Jie Technology Co., Ltd.All Rights Reserved.


 EN
EN 





