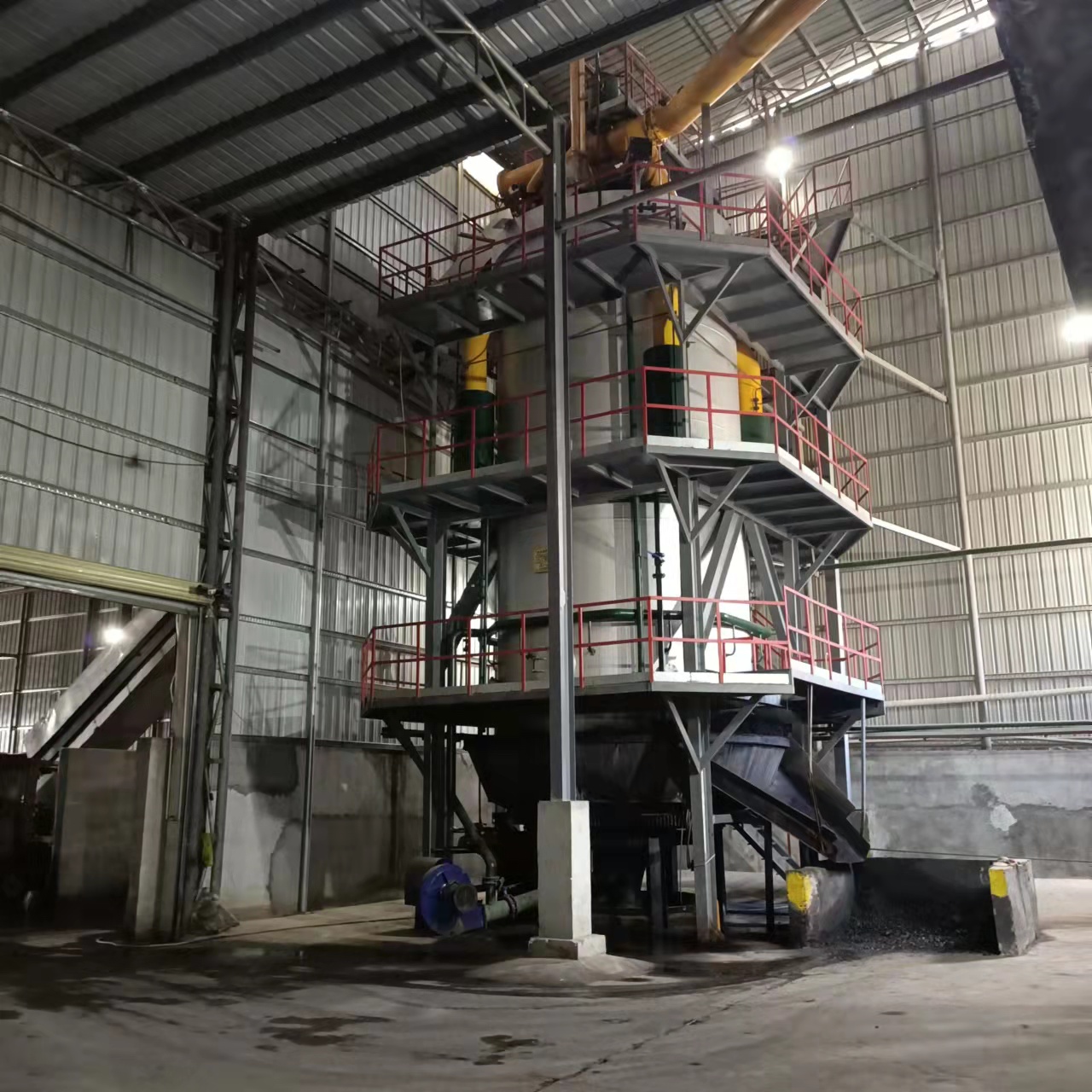
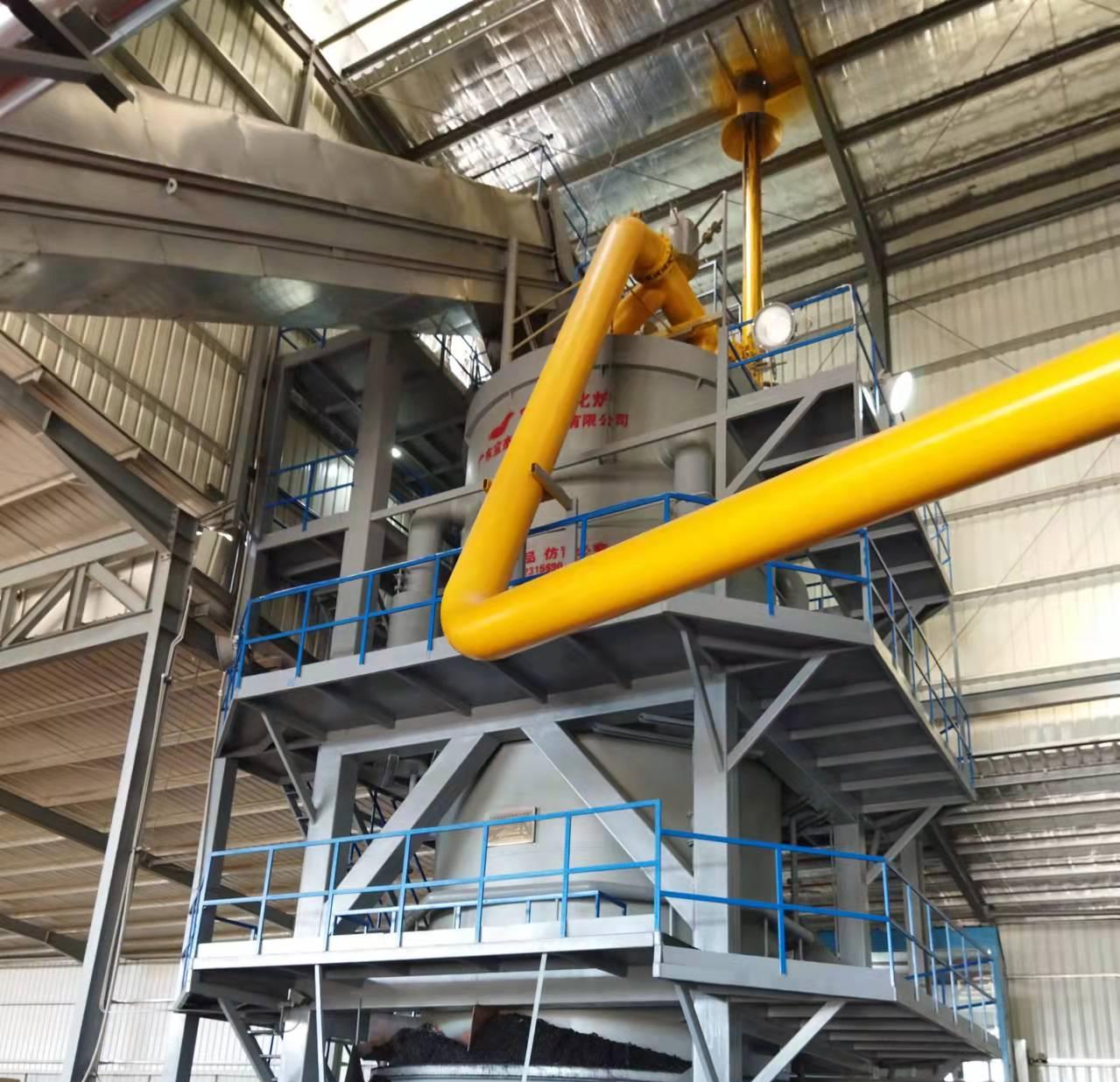
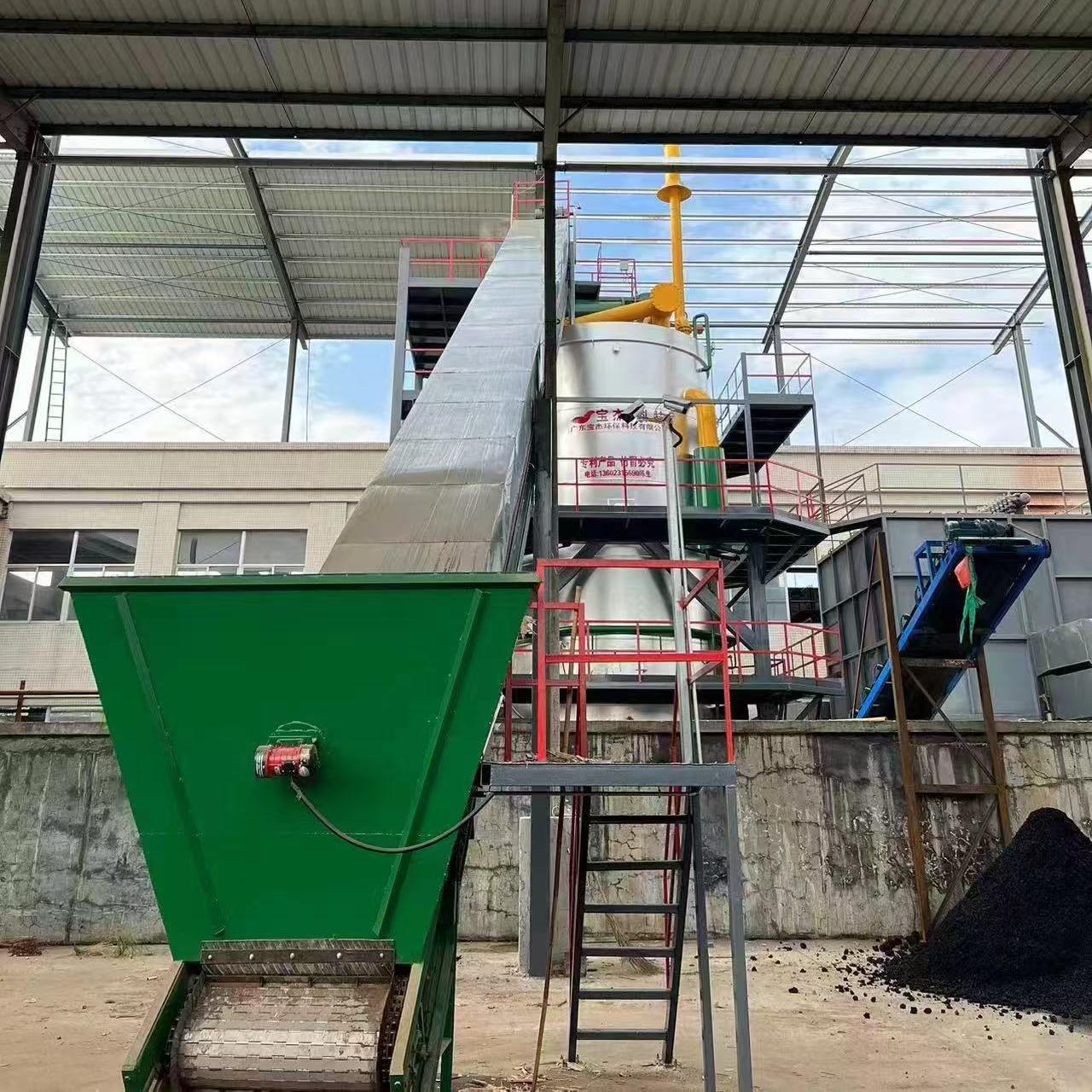
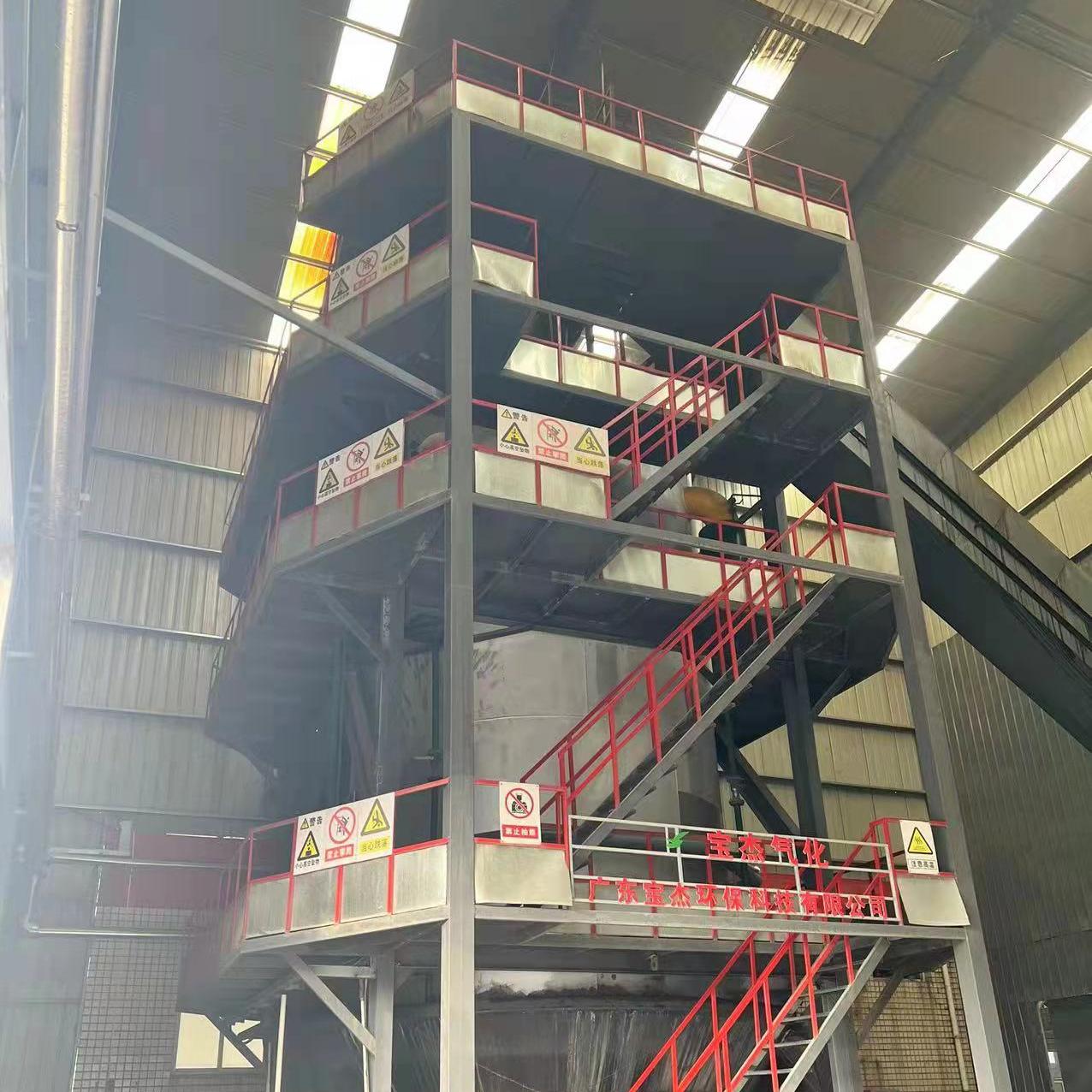
R&D and manufacture of biomass gasification equipment, environmental protection equipment, boiler equipment, investment in heating (steam) energy operation and management.
Tel:+86 0769-82928980
E-mail:[email protected]
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Industry News
What Safety Measures Are Essential When Operating a 10 Ton Insulated Furnace Gas Boiler?
A 10 ton insulated furnace gas boiler is a large-scale industrial boiler commonly used in manufacturing, processing plants, and energy production facilities. While these boilers are highly efficient and capable of generating substantial steam output, they also pose significant safety risks if not operated properly. Gas-fired boilers operate under high pressure and high temperature, and the use of combustible fuel introduces the potential for explosions, fires, and toxic gas exposure. Therefore, implementing comprehensive safety measures is critical for the protection of personnel, equipment, and surrounding facilities.
This article explores the essential safety measures for operating a 10 ton insulated furnace gas boiler, covering operational procedures, maintenance practices, emergency protocols, and regulatory compliance.
1. Understanding the Hazards of Gas Boilers
Before discussing safety measures, it is important to understand the hazards associated with gas boilers:
- High Pressure: Operating at high pressure increases the risk of pipe or vessel rupture if pressure control fails.
- High Temperature: Boiler surfaces and steam can cause severe burns.
- Gas Leaks: Natural gas or liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) leaks can lead to explosions or asphyxiation.
- Carbon Monoxide: Incomplete combustion can produce carbon monoxide, which is toxic and potentially fatal.
- Mechanical Failures: Faulty valves, pumps, or safety devices may result in system malfunctions or accidents.
Recognizing these hazards underscores the need for a rigorous safety approach, including proper installation, operation, monitoring, and maintenance.
2. Proper Installation and Commissioning
Safety begins at the installation phase:
- Professional Installation: Boilers must be installed by certified technicians familiar with industrial gas systems. Incorrect installation can compromise safety controls, pressure relief mechanisms, and gas supply lines.
- Foundation and Insulation: Ensure that the boiler rests on a stable, level foundation. Proper insulation reduces heat loss and prevents accidental contact with hot surfaces.
- Ventilation and Exhaust Systems: Adequate ventilation is crucial for preventing the accumulation of combustible gases. Exhaust chimneys should comply with local emission standards to safely vent combustion by-products.
- Safety Devices: Install pressure relief valves, temperature sensors, gas leak detectors, flame detectors, and automatic shut-off systems during commissioning. These devices are critical for preventing accidents.
3. Operator Training and Competency
Human error is one of the leading causes of boiler accidents. Proper operator training is essential:
- Certification: Operators should have formal training and licensing as required by local regulations.
- Understanding Controls: Operators must be familiar with all boiler controls, alarms, and emergency shut-off procedures.
- Routine Monitoring: Operators should routinely check pressure, water levels, fuel supply, and combustion efficiency.
- Emergency Response: Training must include steps to take in case of gas leaks, fire, or boiler malfunction, including evacuation and alarm protocols.

4. Regular Inspection and Maintenance
Preventive maintenance is crucial for safe boiler operation:
- Daily Checks: Monitor water levels, pressure readings, fuel supply, and flame stability. Any abnormal reading should prompt immediate investigation.
- Weekly and Monthly Maintenance: Inspect and clean burners, fuel lines, pressure relief valves, and safety shut-off devices. Ensure that insulation and refractory linings are intact.
- Annual Overhaul: Conduct a comprehensive inspection of the boiler shell, tubes, furnace lining, and gas connections. Testing of safety valves, gas detectors, and control systems is essential.
- Leak Detection: Use gas detectors and visual inspections to identify potential leaks in fuel supply lines.
- Documentation: Maintain logs of inspections, repairs, and maintenance to ensure accountability and regulatory compliance.
5. Water and Pressure Safety
Proper water management is critical:
- Correct Water Levels: Low water levels can lead to overheating and boiler tube damage, while overfilling can cause water hammer and pressure surges.
- Pressure Relief Valves: Ensure all safety valves are properly calibrated and functional to prevent overpressure conditions.
- Automatic Shut-Off: Modern boilers are equipped with low-water cutoffs and pressure sensors that automatically stop operation if unsafe conditions are detected.
6. Combustion and Gas Safety
Gas-related hazards are particularly dangerous in industrial boilers:
- Gas Leak Detection: Install sensors that continuously monitor for leaks in fuel supply lines.
- Flame Failure Protection: Boilers should have a flame detection system that shuts off gas supply in case the flame is extinguished.
- Combustion Control: Maintain the correct air-to-fuel ratio to prevent incomplete combustion and carbon monoxide production.
- Regular Burner Inspection: Burners should be cleaned and tested regularly to ensure proper ignition and flame stability.
7. Emergency Protocols
Preparedness is critical for mitigating accidents:
- Emergency Shut-Off: Operators must know the location and operation of manual and automatic emergency shut-off systems.
- Fire Safety: Fire extinguishers, fire blankets, and sprinkler systems should be easily accessible. Training should cover fire suppression techniques.
- Evacuation Plans: Clearly marked exits and escape routes should be in place. Employees must be trained in evacuation procedures.
- Communication: Establish clear communication protocols for reporting gas leaks, pressure anomalies, or fires.
8. Insulation and Thermal Safety
High surface temperatures can cause burns:
- Surface Insulation: Insulating the boiler shell and furnace helps prevent accidental contact injuries.
- Warning Signs: Display visible caution signs near hot surfaces.
- Protective Equipment: Operators should wear heat-resistant gloves, helmets, and clothing when working near the boiler.
9. Compliance with Standards and Regulations
Operating a 10 ton gas boiler requires compliance with national and international safety standards:
- Local Boiler Codes: Adhere to building and fire codes related to boiler installation and operation.
- Occupational Safety Regulations: Ensure that workplace safety standards are maintained, including ventilation, fire protection, and personal protective equipment.
- Periodic Certification: Boilers should be inspected and certified periodically by regulatory authorities to ensure compliance with safety standards.
10. Advanced Safety Technologies
Modern boilers incorporate advanced technologies to enhance safety:
- Digital Control Systems: PLC or computerized control systems monitor pressure, temperature, and fuel flow in real time.
- Automatic Shutdown: Integrated systems can automatically stop operation if unsafe conditions are detected.
- Remote Monitoring: Some boilers allow remote monitoring of operational parameters, providing early alerts for anomalies.
- Data Logging: Continuous logging of boiler performance helps identify trends and potential hazards before they become critical.
Conclusion
A 10 ton insulated furnace gas boiler is a powerful and essential piece of industrial equipment. While its operation enables efficient energy production and industrial processes, it also involves significant risks if safety measures are neglected. Ensuring safe operation requires a combination of proper installation, operator training, regular maintenance, water and pressure management, gas safety protocols, emergency preparedness, thermal protection, regulatory compliance, and modern safety technologies.
By implementing these safety measures, industrial facilities can significantly reduce the likelihood of accidents, protect personnel, maintain operational efficiency, and extend the lifespan of the boiler. Safety should never be compromised, as even a single lapse can result in severe injuries, equipment damage, and substantial financial loss.
The key to safe operation is vigilance, regular inspections, continuous training, and strict adherence to both manufacturer guidelines and industry regulations. In doing so, industrial operators can maximize the performance of their 10 ton insulated furnace gas boilers while minimizing risks.
Quick Links
Products
contact Us
 Tel: +86 0769-82928980
Tel: +86 0769-82928980 Fax: [email protected]
Fax: [email protected] E-mail: [email protected]
E-mail: [email protected] Company Address: Dalang Chamber of Commerce Building, No. 288 Yinlang South Road, Dalang Town, Dongguan City 13333, China
Company Address: Dalang Chamber of Commerce Building, No. 288 Yinlang South Road, Dalang Town, Dongguan City 13333, China Factory Add:
West side of Centre Road and south side of Zhongyuan Road within Hongcaoyuan, Hongcao Town, Shanwei Urban District
Factory Add:
West side of Centre Road and south side of Zhongyuan Road within Hongcaoyuan, Hongcao Town, Shanwei Urban District
Copyright© 2022 Guangdong Bao Jie Technology Co., Ltd.All Rights Reserved.


 EN
EN 





