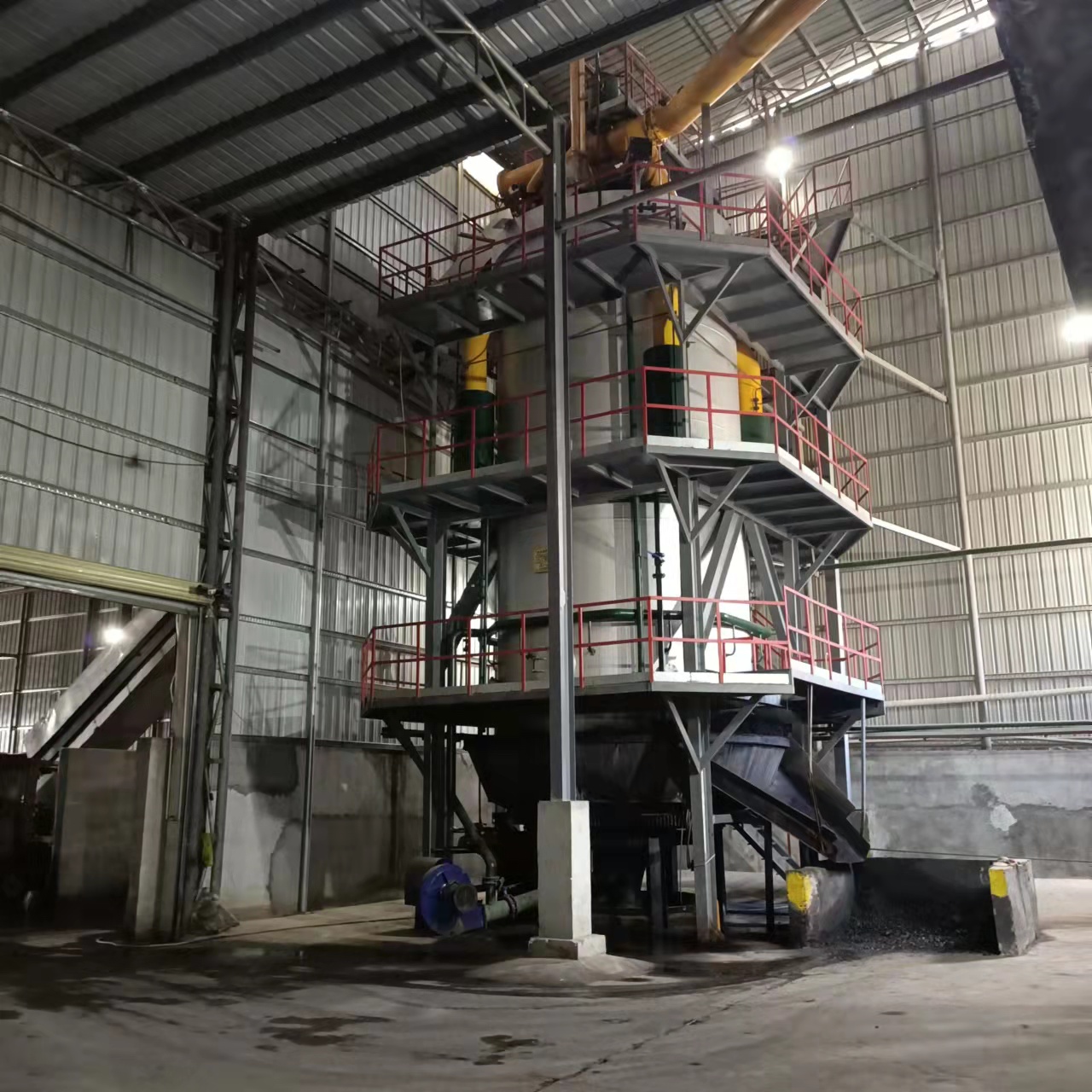
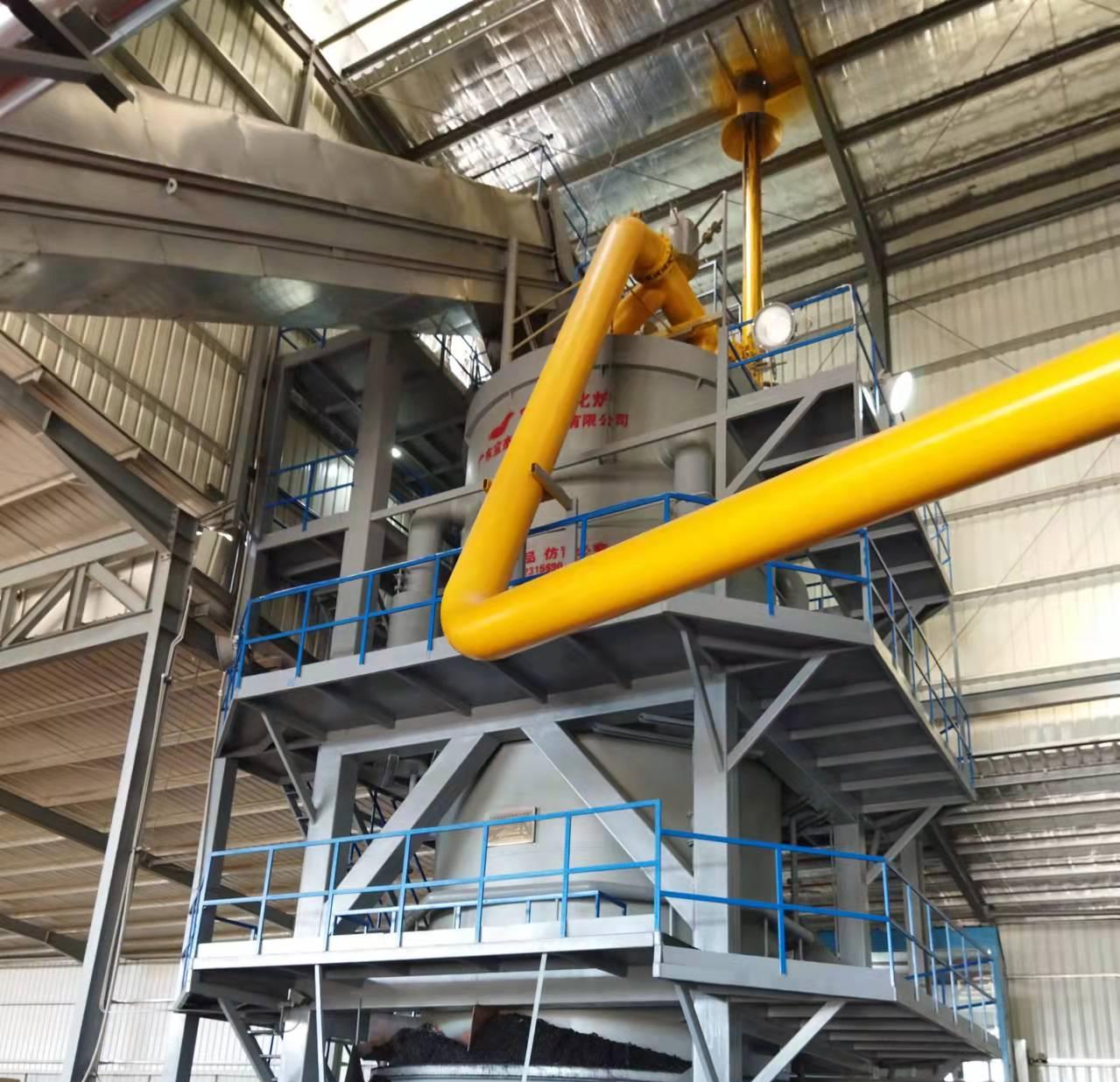
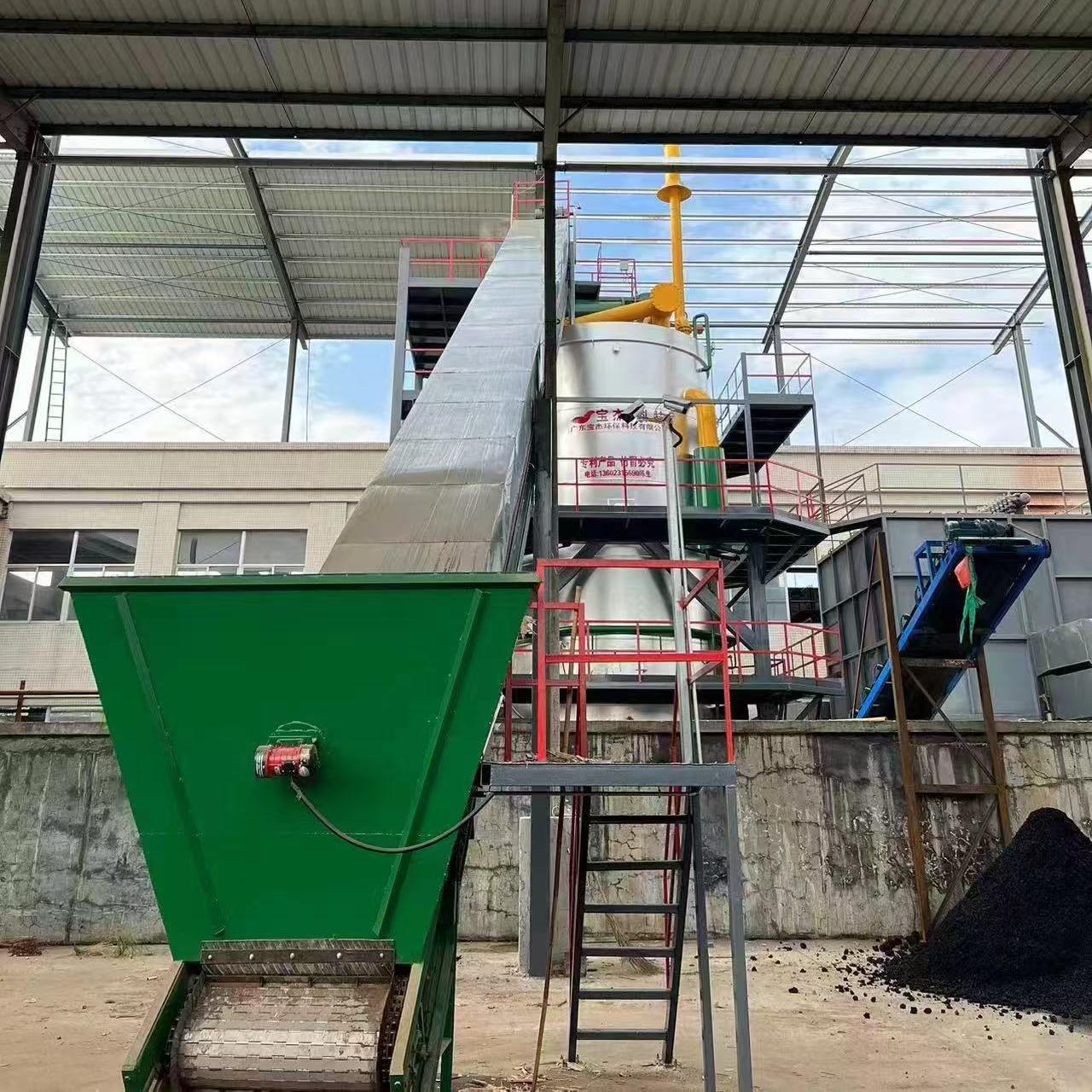
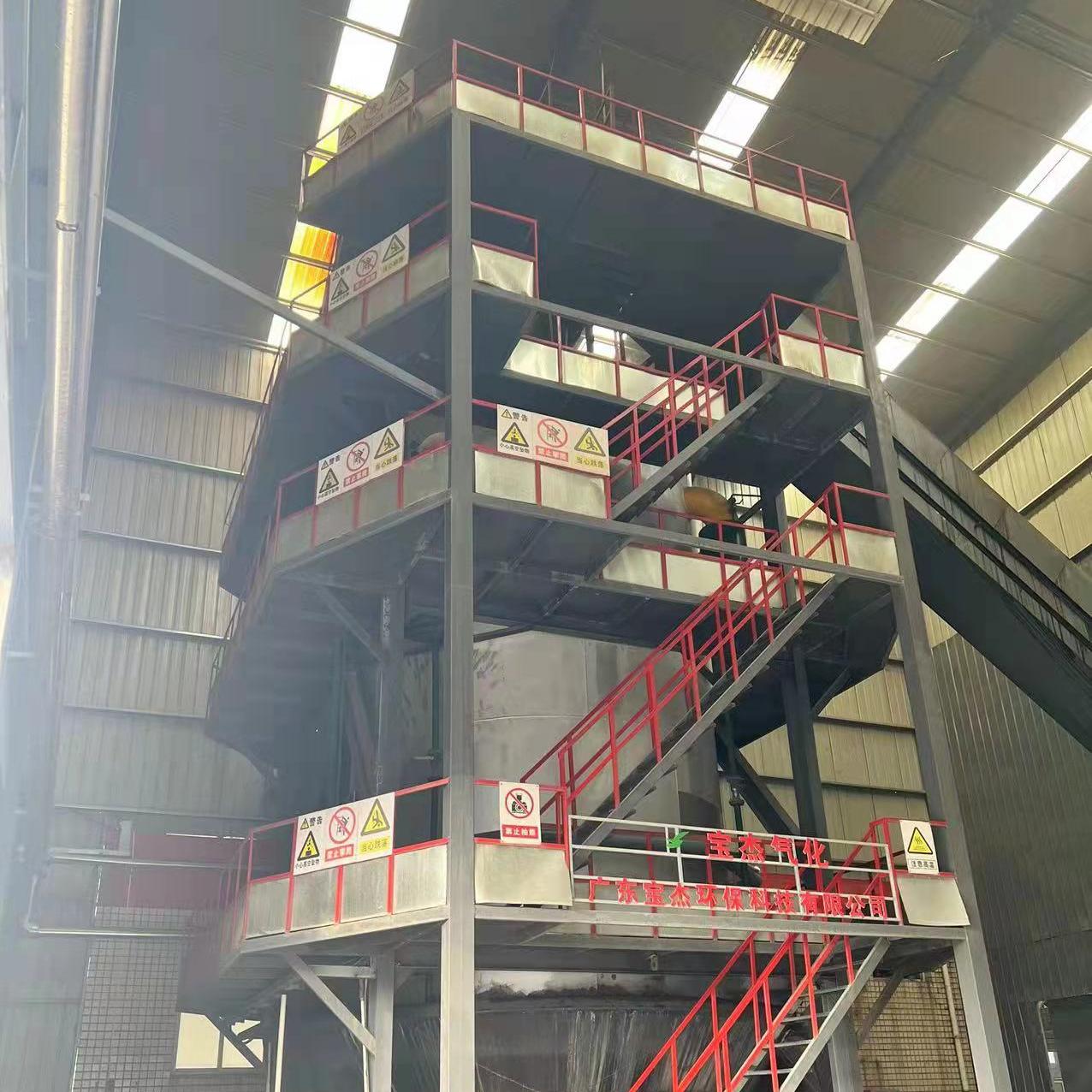
R&D and manufacture of biomass gasification equipment, environmental protection equipment, boiler equipment, investment in heating (steam) energy operation and management.
Tel:+86 0769-82928980
E-mail:[email protected]
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Industry News
What Are the Benefits and Applications of Biomass Gasification in Sustainable Energy?
As the world faces growing environmental concerns and the need for sustainable energy sources, biomass gasification has emerged as an innovative and promising technology for converting organic waste into valuable energy. Biomass gasification is a process that produces synthetic gas (syngas) by heating organic materials in a controlled, low-oxygen environment. This syngas can then be used to generate electricity, heat, or even biofuels.
The resulting syngas can be used as a fuel for various applications, including electricity generation, heating, and the production of biofuels. Biomass gasification offers a clean, renewable energy source by utilizing waste materials that would otherwise decompose in landfills and produce harmful greenhouse gases.
The Biomass Gasification Process
The process of biomass gasification occurs in several stages:
Drying: The biomass material is dried to remove moisture content, making it more suitable for gasification. This is typically done through heat or air circulation.
Pyrolysis: The dried biomass is then heated to temperatures between 300°C and 500°C, causing it to decompose into volatile gases, oils, and charcoal. This stage is crucial for the creation of syngas.
Gasification: In this stage, the material is heated further in a low-oxygen environment. The process causes chemical reactions to occur, breaking down the biomass into syngas, which consists of gases like carbon monoxide and hydrogen.
Syngas Cleaning: The syngas produced contains impurities such as tar, particulates, and trace gases that must be removed before it can be used for energy production. A cleaning system ensures that the syngas is purified and ready for use.
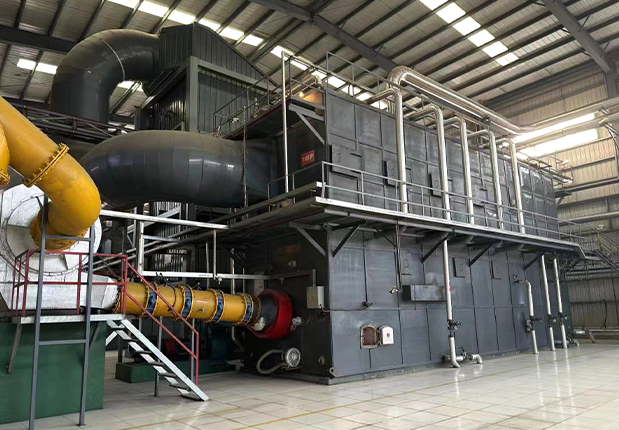

Power Generation or Biofuel Production: The cleaned syngas can be used in engines, turbines, or fuel cells to generate electricity. Alternatively, it can be converted into biofuels like ethanol or synthetic diesel, providing an additional renewable energy source.
Benefits of Biomass Gasification
Renewable Energy Source Biomass gasification relies on renewable organic materials, such as wood, agricultural residues, and waste from food processing, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels. By converting waste into useful energy, biomass gasification reduces dependence on non-renewable energy sources.
Waste Management Biomass gasification can significantly reduce the amount of organic waste that ends up in landfills. Waste materials that would otherwise release harmful greenhouse gases as they decompose are instead converted into clean energy. This not only helps to tackle the waste crisis but also reduces the environmental impact of landfills.
Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions Unlike fossil fuels, biomass is considered a carbon-neutral energy source. Although burning biomass does release carbon dioxide, the plants and organic materials used in the process have absorbed CO2 during their growth. This creates a closed-loop system, meaning that the net increase in CO2 emissions is minimal.
Energy Security Biomass gasification can enhance energy security by providing a local, decentralized energy solution. Biomass resources are often locally available, and gasification plants can be built near waste sources, reducing the need for long-distance transportation and making communities more self-sufficient in their energy needs.
Versatile Application The syngas produced from biomass gasification can be used for a wide range of applications. It can power industrial machinery, generate electricity for homes and businesses, provide heat for homes and greenhouses, and even be converted into biofuels for transportation.
Electricity Generation Biomass gasification is increasingly being used to generate electricity in power plants. The syngas produced from gasification is burned in gas engines or turbines to generate electricity, providing an alternative to coal or natural gas-fired power plants. This application is especially beneficial in rural areas where biomass resources are abundant.
Industrial Heat Production Many industries, including paper mills, food processing plants, and textile factories, use heat for their es. Biomass gasification provides a sustainable and cost-effective way to meet these heating needs. The heat generated can also be used in cogeneration systems to produce both heat and electricity.
Biofuel Production Syngas produced through biomass gasification can be converted into biofuels, such as ethanol or synthetic diesel, through further chemical processes. This allows biomass gasification to contribute to the development of cleaner transportation fuels and reduce the reliance on conventional gasoline and diesel.
Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Systems In some applications, biomass gasification systems are used in combined heat and power (CHP) systems. CHP systems generate both electricity and useful heat from a single energy source, increasing overall energy efficiency and reducing waste.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While biomass gasification offers many benefits, there are some challenges to its widespread adoption. The technology requires significant investment in infrastructure and equipment, particularly in the development of efficient gasifiers and syngas cleaning systems. Additionally, there may be competition for biomass resources with other sectors, such as the biofuel and paper industries, which could affect the availability of raw materials.
However, ongoing research and technological advancements are addressing these challenges, and biomass gasification is expected to play a larger role in the future of renewable energy. With its potential to provide clean, sustainable energy from waste materials, biomass gasification is poised to contribute to the global transition toward a more sustainable and circular economy.
Quick Links
Products
contact Us
 Tel: +86 0769-82928980
Tel: +86 0769-82928980 Fax: [email protected]
Fax: [email protected] E-mail: [email protected]
E-mail: [email protected] Company Address: Dalang Chamber of Commerce Building, No. 288 Yinlang South Road, Dalang Town, Dongguan City 13333, China
Company Address: Dalang Chamber of Commerce Building, No. 288 Yinlang South Road, Dalang Town, Dongguan City 13333, China Factory Add:
West side of Centre Road and south side of Zhongyuan Road within Hongcaoyuan, Hongcao Town, Shanwei Urban District
Factory Add:
West side of Centre Road and south side of Zhongyuan Road within Hongcaoyuan, Hongcao Town, Shanwei Urban District
Copyright© 2022 Guangdong Bao Jie Technology Co., Ltd.All Rights Reserved.


 EN
EN 





