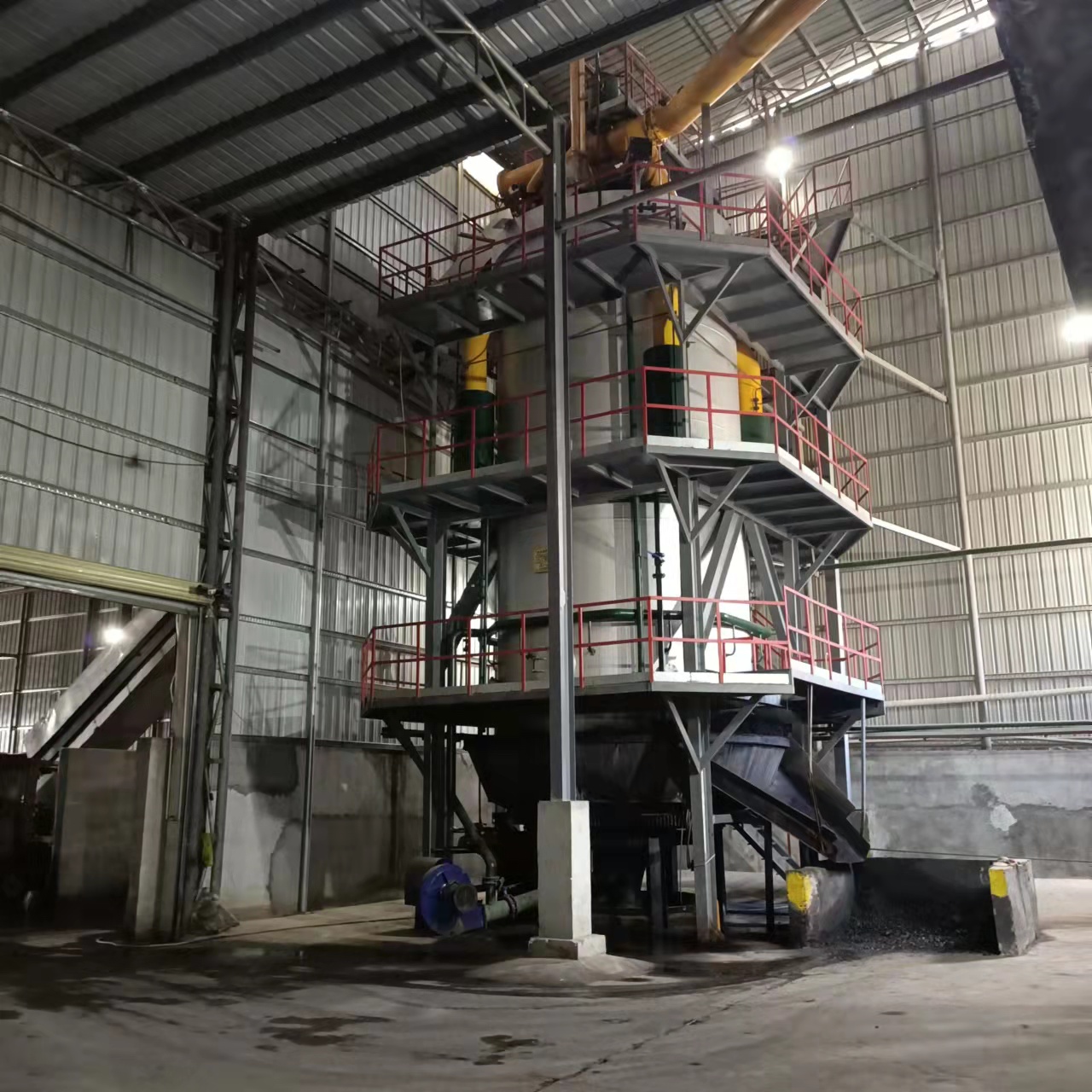
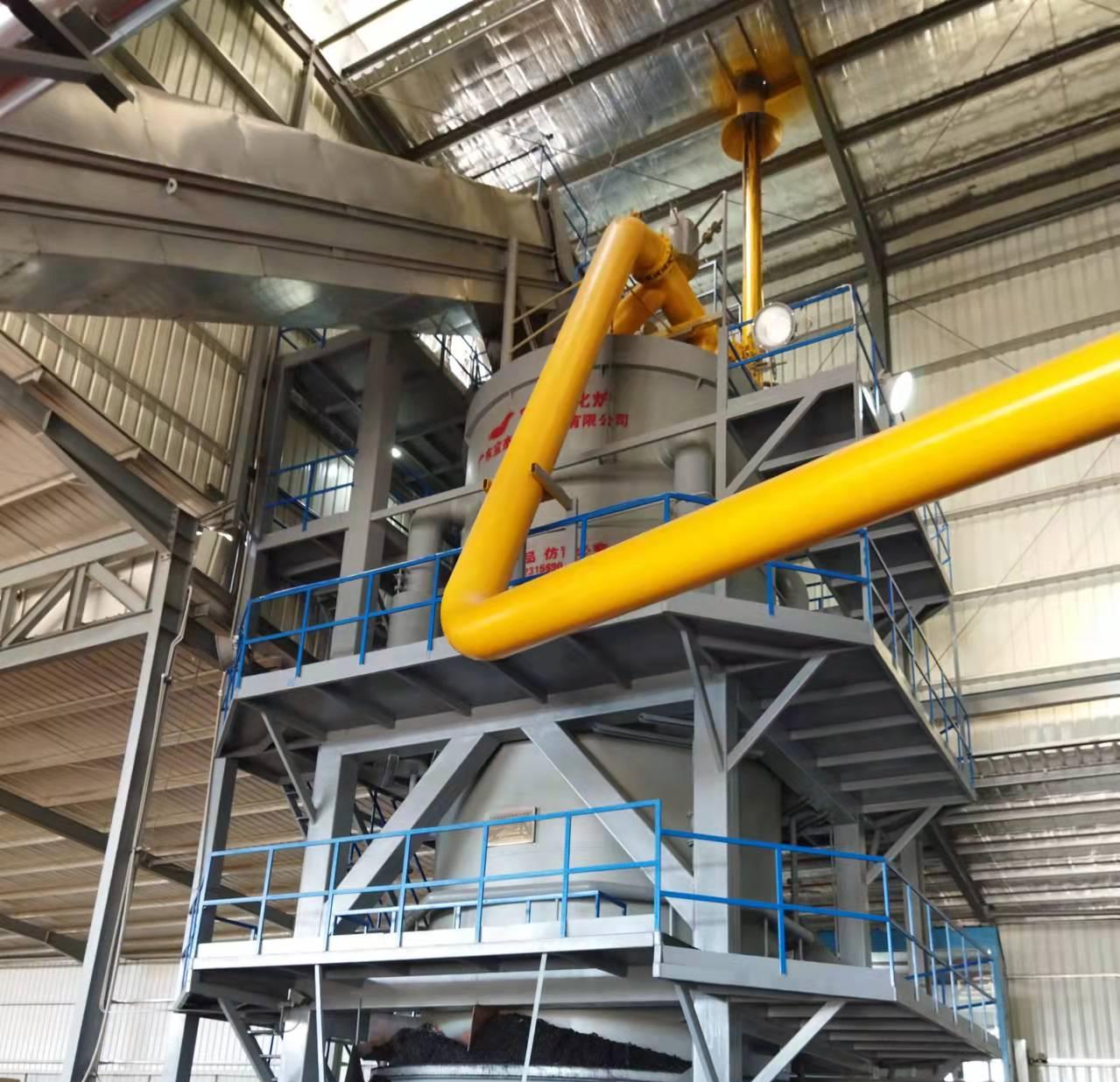
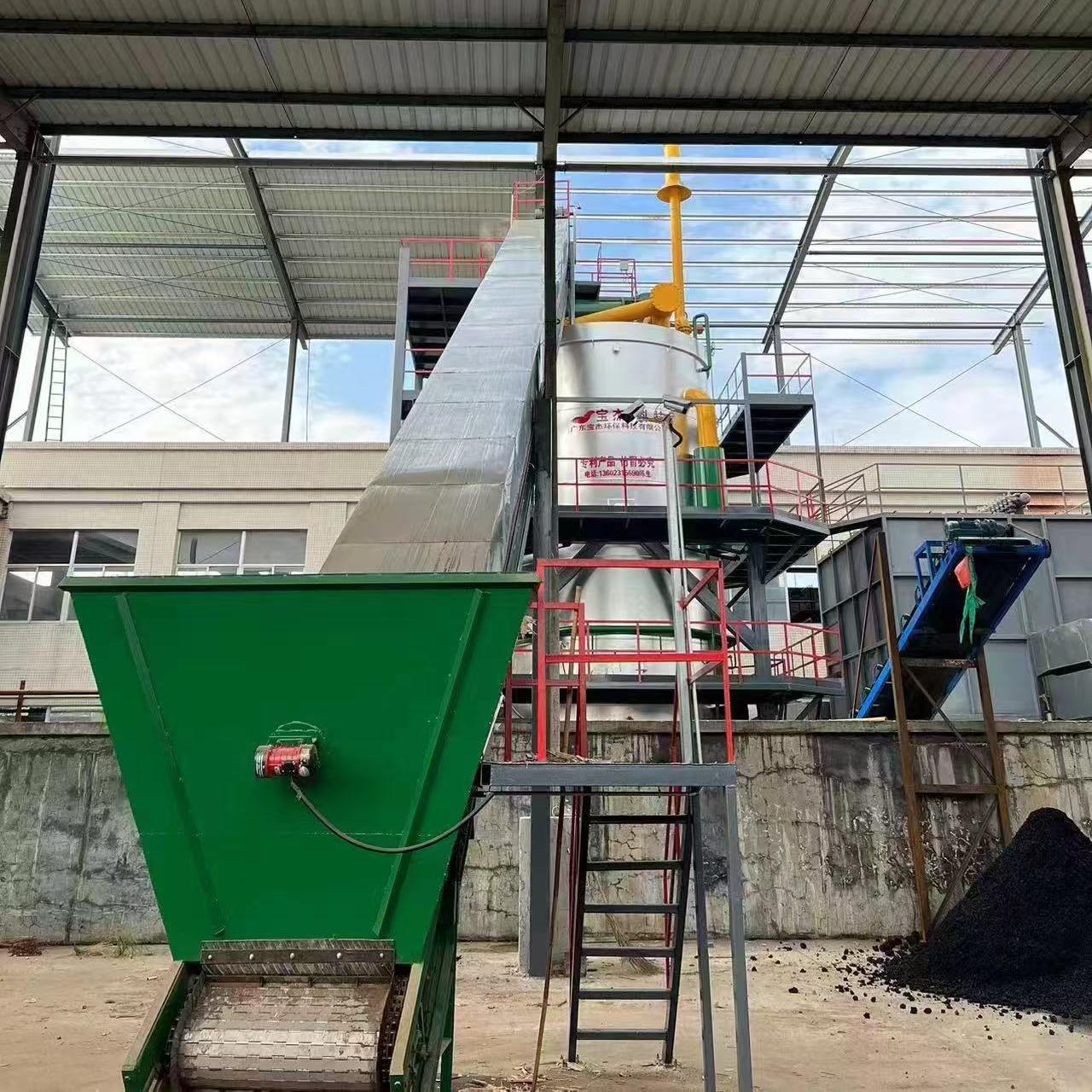
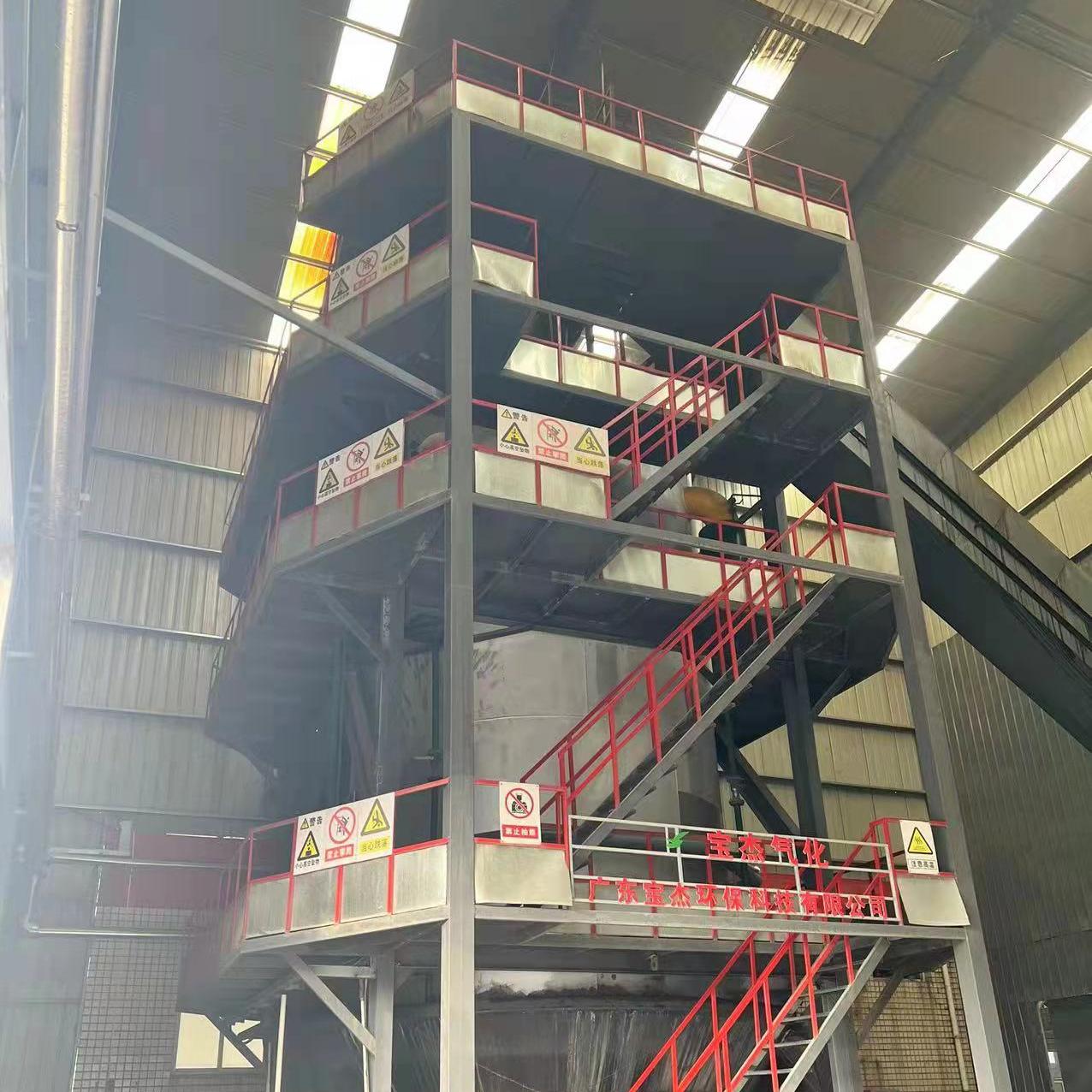
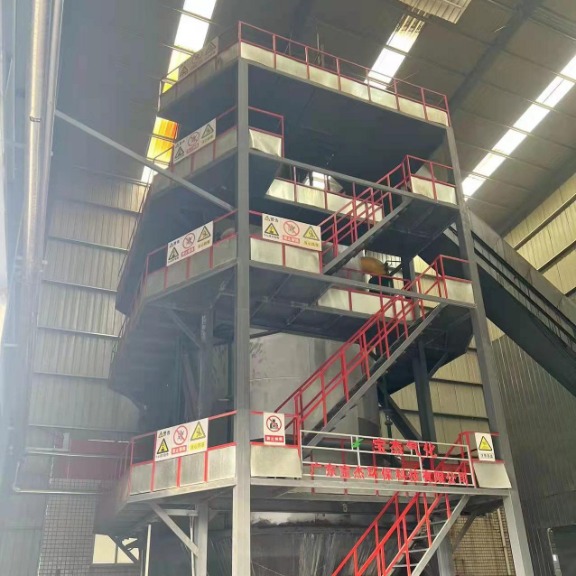
R&D and manufacture of biomass gasification equipment, environmental protection equipment, boiler equipment, investment in heating (steam) energy operation and management.
Tel:+86 0769-82928980
E-mail:[email protected]
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Industry News
Harnessing Clean Energy: The Potential of Biomass Gas in a Sustainable Future
As the global demand for clean and renewable energy continues to rise, biomass gas is emerging as a promising alternative to fossil fuels. Derived from organic materials such as agricultural waste, forestry residues, and even household garbage, biomass gas offers a sustainable way to generate heat, electricity, and even transportation fuel.
With its potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, support rural economies, and provide decentralized energy solutions, biomass gas is gaining attention as a key player in the transition to a greener energy landscape.
There are two main types:
Biogas : Produced via anaerobic digestion , where microorganisms break down biodegradable material in the absence of oxygen.
Syngas : Generated through gasification , a high-temperature process that converts solid biomass into a combustible gas mixture.
Both forms can be used for power generation, heating, and as a feedstock for producing liquid fuels or chemicals.
1. Anaerobic Digestion
This process involves placing organic waste (such as manure, food scraps, or sewage) into an enclosed tank called a digester . In this oxygen-free environment, bacteria break down the material, releasing methane (CH₄) and carbon dioxide (CO₂) — the primary components of biogas.
The resulting biogas can be cleaned and upgraded for use in generators, boilers, or even injected into natural gas grids.
2. Gasification
In gasification, dried biomass is heated to high temperatures (600–1000°C) with a controlled amount of oxygen or steam. This causes the material to break down into hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), and methane — collectively known as syngas.
Syngas can be used in internal combustion engines, turbines, or further processed into synthetic fuels via the Fischer-Tropsch process .
Key Benefits of Biomass Gas
Renewable & Sustainable
Made from organic waste, reducing landfill use and methane emissions from decomposition.
Carbon Neutral

The CO₂ released during combustion is offset by the CO₂ absorbed by plants during their growth cycle.
Waste-to-Energy Solution
Turns agricultural, industrial, and municipal waste into usable energy.
Energy Independence
Can be produced locally, supporting rural development and off-grid communities.
Versatile Applications
Used for electricity generation, vehicle fuel (after upgrading to biomethane), district heating, and industrial processes.
Supports Circular Economy
Residual materials like digestate (from anaerobic digestion) can be used as organic fertilizer.
Common Applications
Power Generation : Biogas and syngas can fuel combined heat and power (CHP) systems.
Transportation Fuel : After purification, biomass gas can be compressed and used as a substitute for CNG (Compressed Natural Gas).
Industrial Heating : Used in manufacturing sectors needing consistent heat supply.
Agricultural Use : Farms can utilize biogas from animal manure to generate energy and improve waste management.
Municipal Waste Management : Cities can convert organic waste into energy through centralized biogas plants.
As the world moves toward decarbonization and cleaner energy sources, biomass gas stands out as a versatile and environmentally friendly option. It not only provides a solution to managing organic waste but also contributes to energy security and climate protection.
With continued innovation and policy support, biomass gas has the potential to play a significant role in building a more sustainable, low-carbon future.
Quick Links
Products
contact Us
 Tel: +86 0769-82928980
Tel: +86 0769-82928980 Fax: [email protected]
Fax: [email protected] E-mail: [email protected]
E-mail: [email protected] Company Address: Dalang Chamber of Commerce Building, No. 288 Yinlang South Road, Dalang Town, Dongguan City 13333, China
Company Address: Dalang Chamber of Commerce Building, No. 288 Yinlang South Road, Dalang Town, Dongguan City 13333, China Factory Add:
West side of Centre Road and south side of Zhongyuan Road within Hongcaoyuan, Hongcao Town, Shanwei Urban District
Factory Add:
West side of Centre Road and south side of Zhongyuan Road within Hongcaoyuan, Hongcao Town, Shanwei Urban District
Copyright© 2022 Guangdong Bao Jie Technology Co., Ltd.All Rights Reserved.


 EN
EN 





