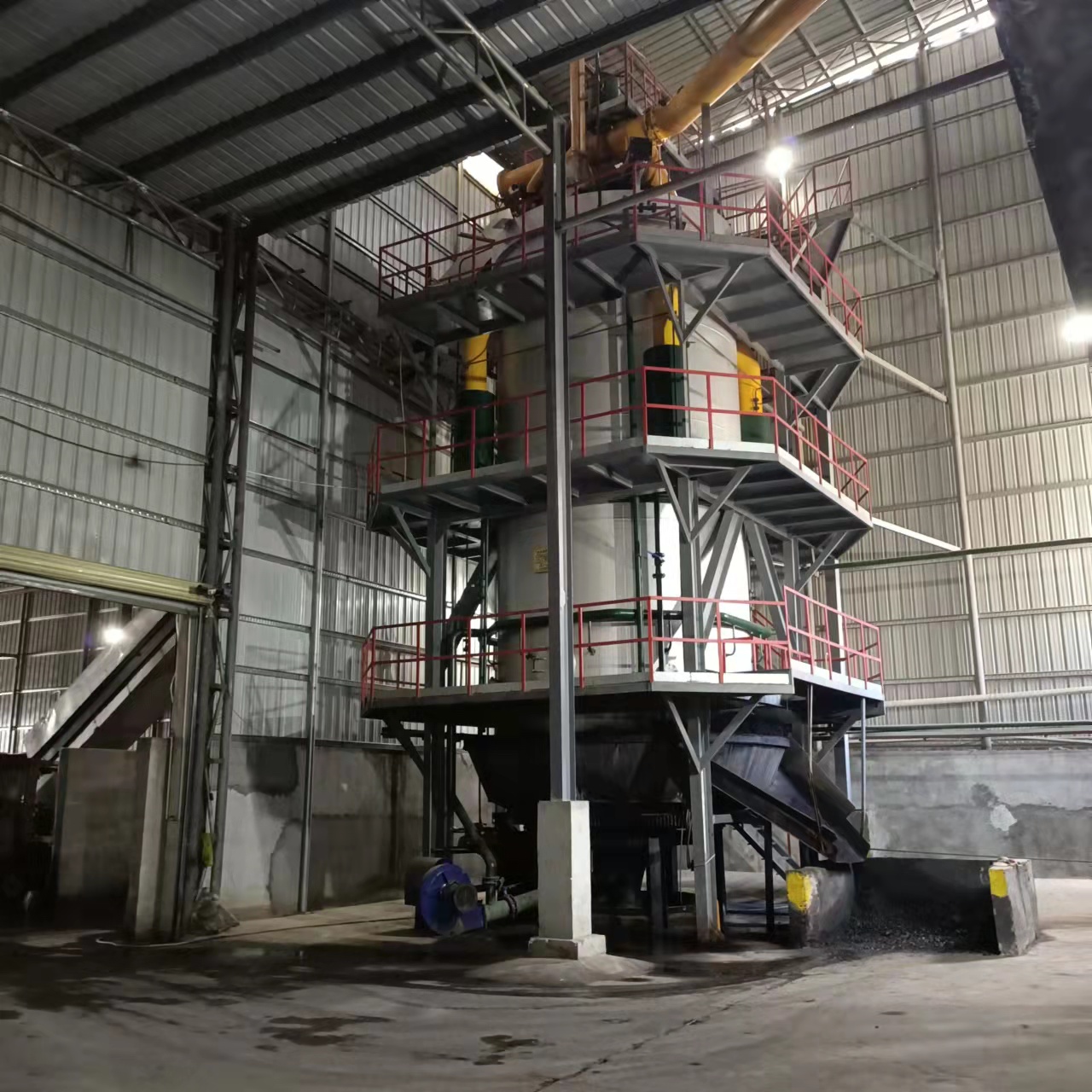
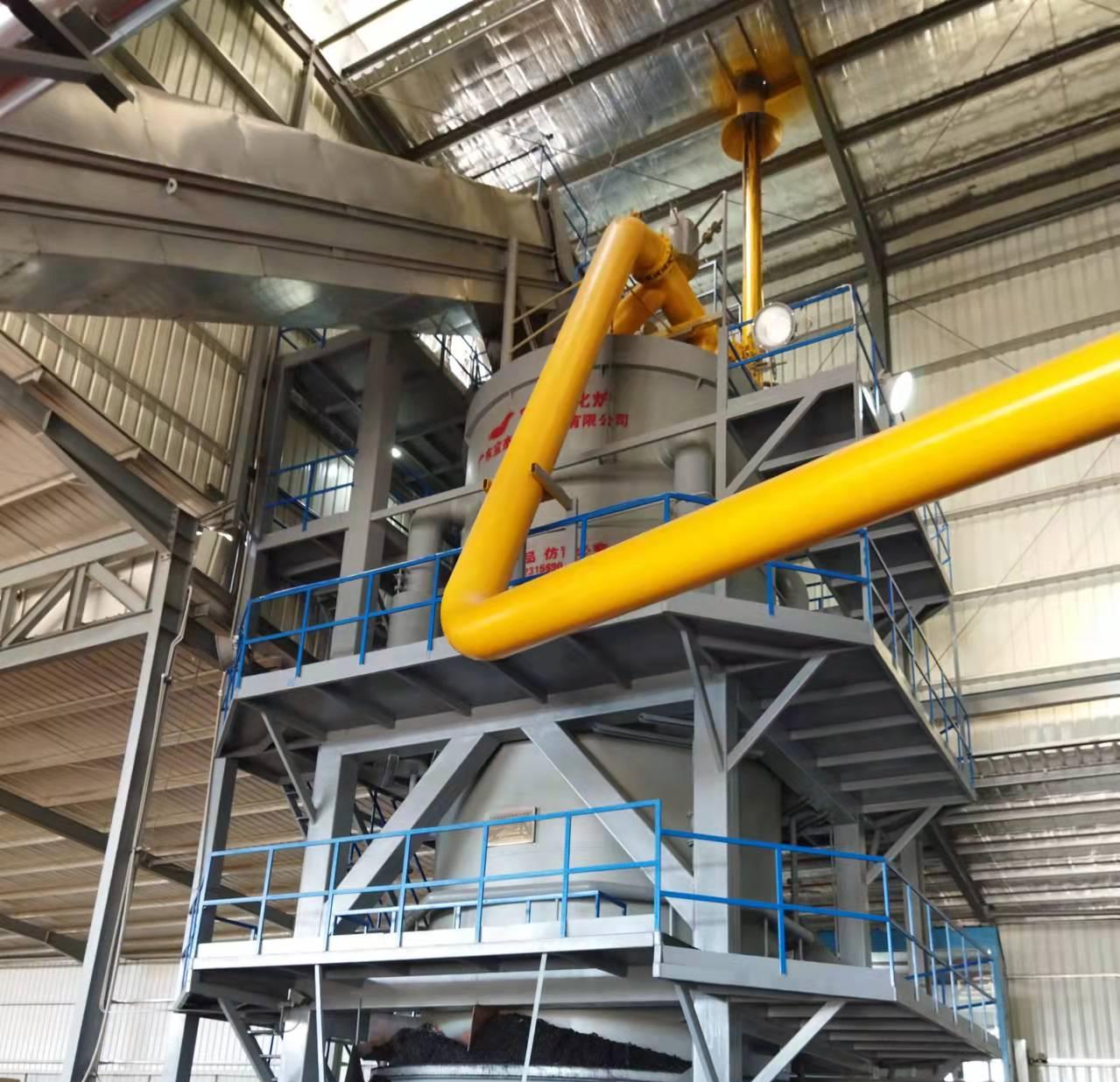
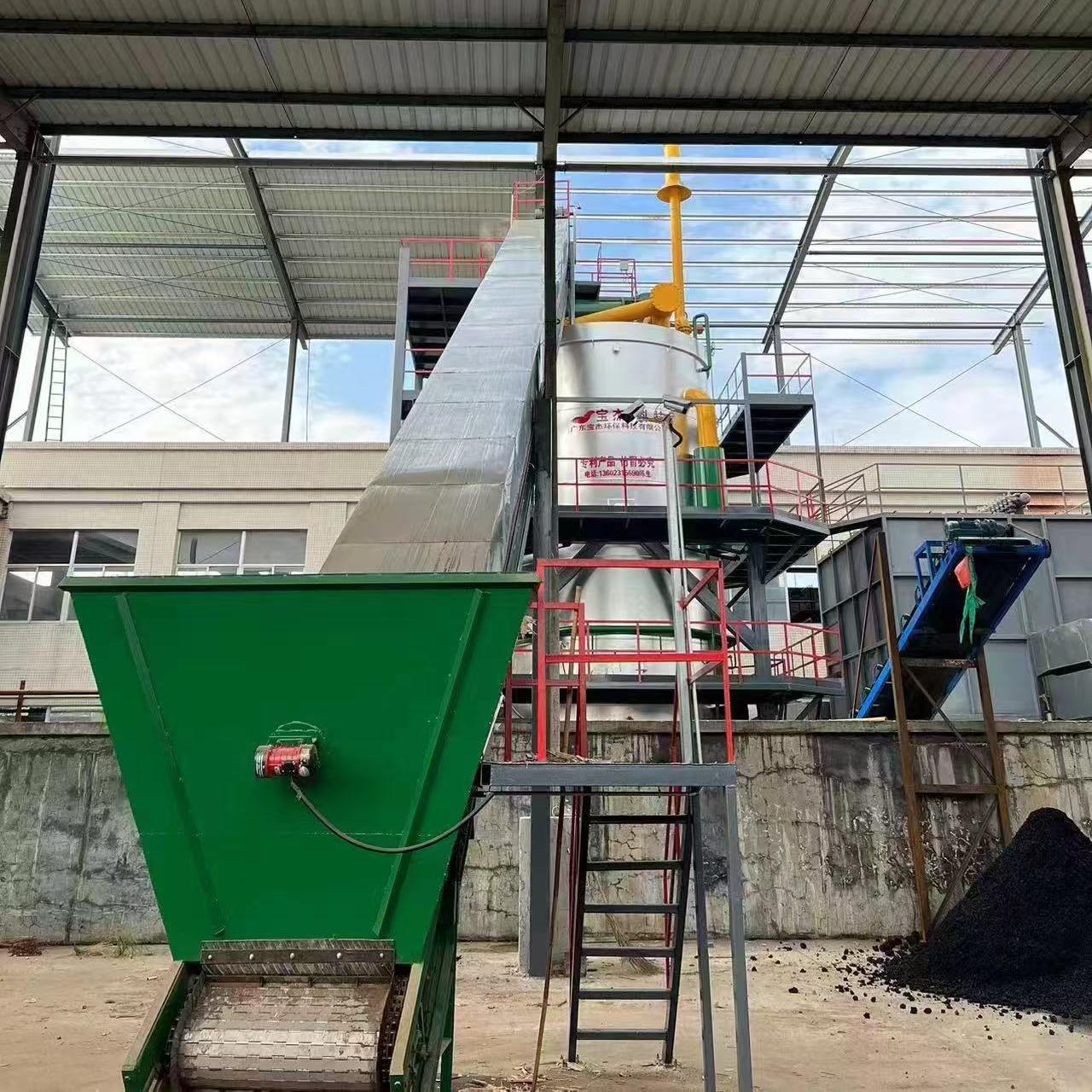
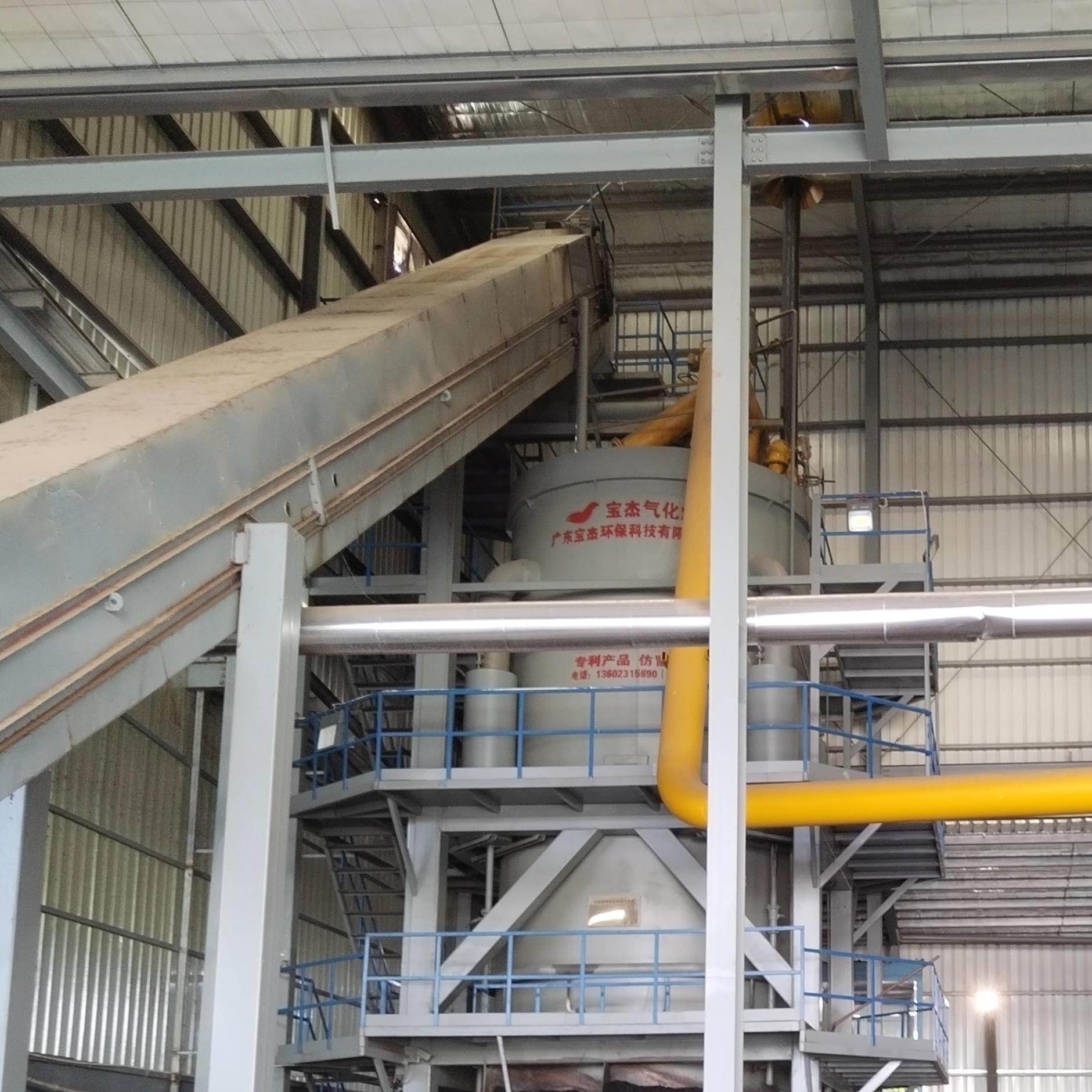
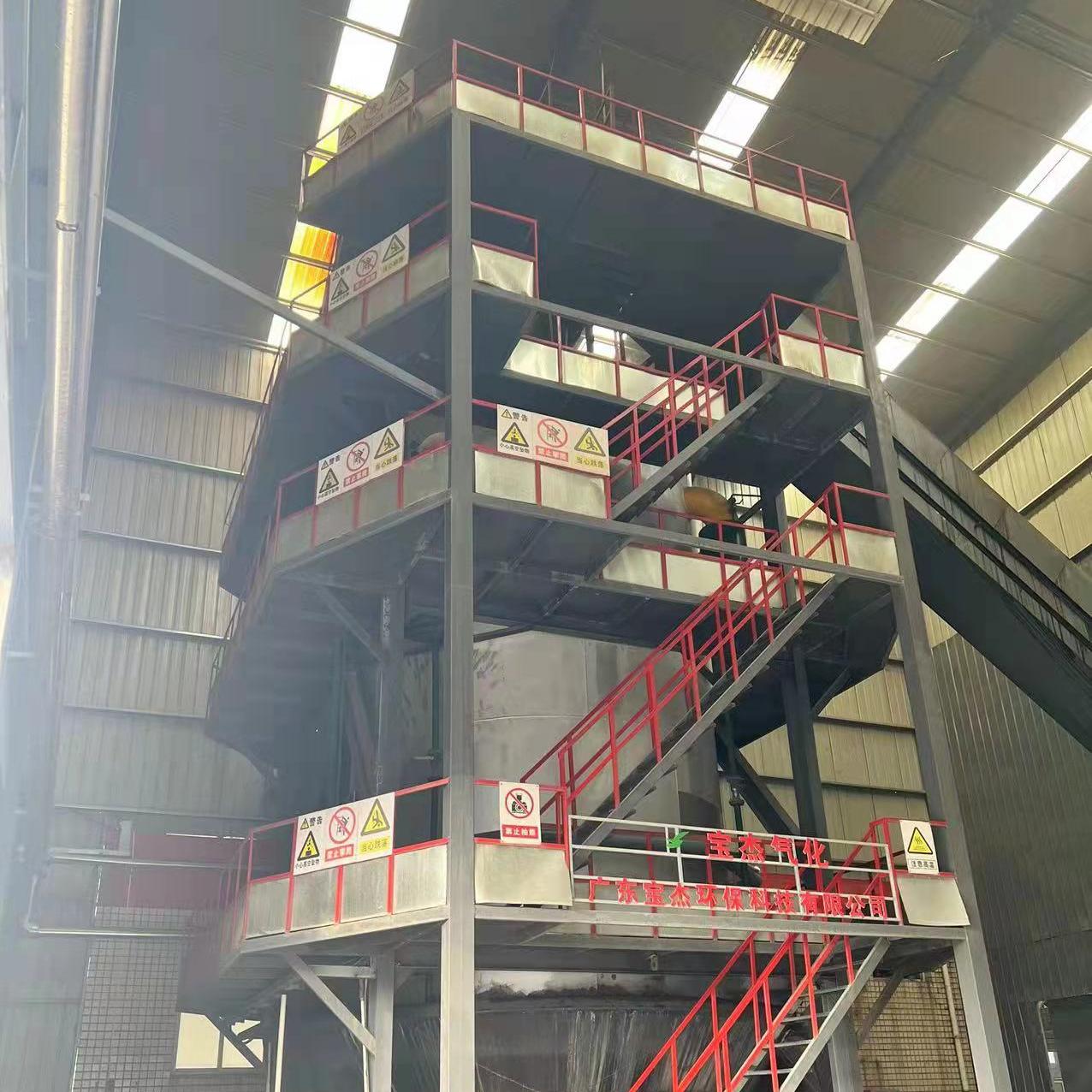
R&D and manufacture of biomass gasification equipment, environmental protection equipment, boiler equipment, investment in heating (steam) energy operation and management.
Tel:+86 0769-82928980
E-mail:[email protected]
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Industry News
What Makes a 20-Tonne Biomass Gasifier a Sustainable Solution for Clean Energy?
In today’s energy landscape, the demand for sustainable and renewable energy technologies has never been higher. Among these innovations, biomass gasifiers stand out as a promising solution that transforms organic materials into clean, efficient fuel. Specifically, the 20-tonne biomass gasifier has gained increasing attention due to its scalability, environmental benefits, and ability to serve industrial power needs. But what exactly makes this system such a valuable tool in the transition toward renewable energy? Let’s take a closer look.
What Is a Biomass Gasifier and How Does It Work?
A biomass gasifier is an advanced energy conversion system that converts organic materials such as agricultural residues, wood chips, sawdust, or municipal solid waste into a combustible gas known as producer gas or syngas. This gas can be used to generate electricity, heat, or even refined into biofuels.
The working principle involves a thermochemical process carried out in limited oxygen conditions. The key stages are:
- Drying: Biomass is first dried to remove moisture, improving efficiency.
- Pyrolysis: The dried biomass is heated to high temperatures, breaking down into volatile gases, tars, and charcoal.
- Combustion: A controlled amount of air or oxygen is introduced to partially burn the biomass, generating heat.
- Reduction: The gases pass through a reduction zone, producing carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H₂), and methane (CH₄)—the main components of syngas.
The 20-tonne biomass gasifier refers to a system capable of processing 20 tonnes of biomass feedstock per day, generating a significant amount of renewable energy suitable for medium to large-scale industries.
Why Choose a 20-Tonne Biomass Gasifier Over Smaller or Larger Models?
The 20-tonne capacity offers a balanced solution between operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Smaller units may not produce enough power for industrial use, while very large systems can require significant capital investment and complex logistics.
Advantages of the 20-tonne system include:
- Optimal scale: Suitable for small cities, manufacturing plants, or industrial parks.
- Flexibility in feedstock: Can handle a variety of local biomass resources such as rice husk, corn stalks, coconut shells, or sawdust.
- Moderate footprint: Compact design compared to traditional biomass power plants.
- Ease of maintenance: Simple mechanical structure with fewer moving parts.
This makes the 20-tonne model an ideal choice for regions seeking energy independence and carbon reduction without investing in massive infrastructure.
What Are the Main Components of a 20-Tonne Biomass Gasifier System?
A modern biomass gasifier includes several integrated components that work together to ensure stable and efficient gas production:
- Feedstock Handling System: Prepares and transports biomass materials into the gasifier.
- Gasification Reactor: The heart of the system where the conversion takes place.
- Cyclone Separator: Removes solid particles such as ash or char from the gas stream.
- Gas Cooling and Cleaning Unit: Reduces the temperature of the gas and eliminates tar, dust, and impurities.
- Gas Storage or Engine System: Stores or directly utilizes the clean syngas for power generation through internal combustion engines or turbines.
Each part plays a critical role in ensuring continuous operation, energy efficiency, and environmental safety.
How Does the 20-Tonne Biomass Gasifier Benefit the Environment?
The environmental benefits of this system are among its most significant advantages. Unlike fossil fuels, biomass is a carbon-neutral energy source. This means that the CO₂ emitted during gasification roughly equals the amount absorbed by plants during their growth cycle.
Key environmental benefits include:
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions compared to coal or diesel.
- Efficient waste management, utilizing agricultural and forestry residues that would otherwise decompose and release methane.
- Lower particulate pollution through controlled combustion and advanced filtration systems.
- Sustainable carbon cycle, promoting renewable energy ecosystems.
Furthermore, when integrated with carbon capture technologies, biomass gasifiers can even achieve negative emissions, contributing to climate mitigation goals.
What Are the Economic and Industrial Applications?
The 20-tonne biomass gasifier serves multiple sectors due to its adaptability and efficiency. Some common applications include:
- Electricity generation for industrial facilities or rural electrification projects.
- Thermal energy production for drying, heating, or steam generation.
- Cogeneration (CHP) systems that produce both power and heat simultaneously.
- Feedstock for bio-refineries, enabling the production of synthetic fuels or chemicals.
Industries such as textiles, paper manufacturing, food processing, and metalworks often adopt biomass gasifiers to reduce their dependence on expensive fossil fuels. Over time, the investment in a 20-tonne system can result in significant cost savings and energy security.
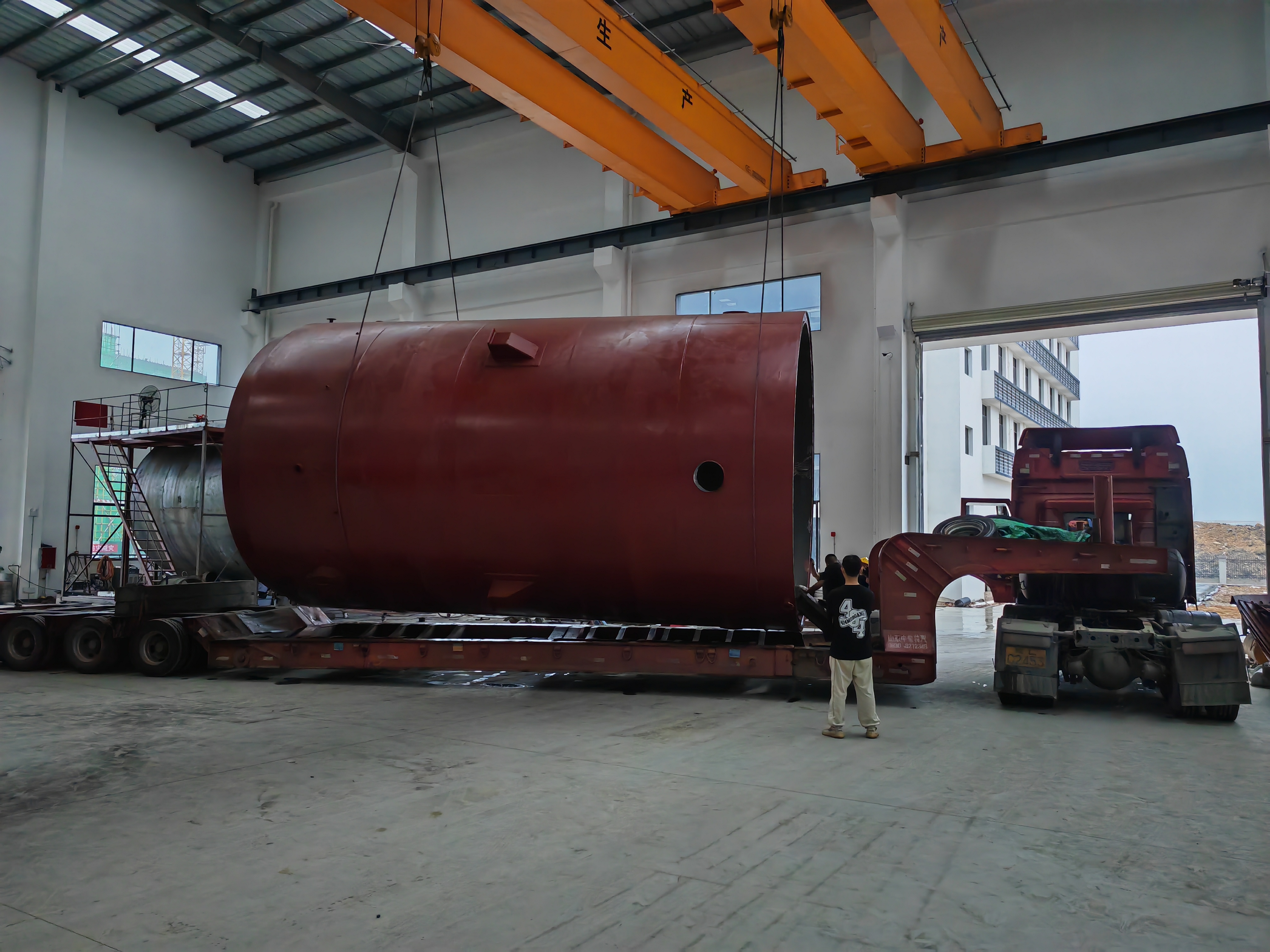

What Are the Technical Challenges and Future Prospects?
Although biomass gasification offers many advantages, several technical challenges still limit its widespread adoption. These include:
- Feedstock variability: Different biomass types have varying moisture content, calorific values, and ash characteristics.
- Tar formation: One of the biggest technical issues that can clog engines and reduce efficiency.
- Maintenance requirements: Regular cleaning and inspection are necessary to prevent operational downtime.
However, technological advancements are rapidly addressing these challenges. Innovations such as plasma-assisted gasification, catalytic tar cracking, and AI-based process monitoring are improving gas quality and reliability.
In the coming years, the 20-tonne biomass gasifier is expected to evolve into a smarter, more automated system integrated with digital sensors and control algorithms for optimized performance.
Is the 20-Tonne Biomass Gasifier the Future of Renewable Energy?
Given the growing global emphasis on sustainability and net-zero targets, biomass gasifiers are emerging as a key transitional technology bridging traditional and renewable energy sources. The 20-tonne model, in particular, fits perfectly within the medium-scale industrial segment—large enough to make an impact but small enough to deploy locally.
When coupled with government incentives, carbon credits, and circular economy principles, these systems can significantly contribute to energy decentralization and rural development. In developing countries, especially, biomass gasifiers can play a transformative role by turning agricultural waste into clean energy, fostering green jobs and economic resilience.
Conclusion
A 20-tonne biomass gasifier represents a powerful blend of environmental responsibility, technological innovation, and economic practicality. It allows industries and communities to harness the energy potential of waste materials, reducing dependence on fossil fuels while minimizing environmental impact.
By turning local biomass into a reliable source of clean energy, this system answers one of the most pressing questions of our time: How can we meet our growing energy needs without harming the planet?
The 20-tonne biomass gasifier stands as a compelling answer—clean, renewable, and ready to power a sustainable future.
Quick Links
Products
contact Us
 Tel: +86 0769-82928980
Tel: +86 0769-82928980 Fax: [email protected]
Fax: [email protected] E-mail: [email protected]
E-mail: [email protected] Company Address: Dalang Chamber of Commerce Building, No. 288 Yinlang South Road, Dalang Town, Dongguan City 13333, China
Company Address: Dalang Chamber of Commerce Building, No. 288 Yinlang South Road, Dalang Town, Dongguan City 13333, China Factory Add:
West side of Centre Road and south side of Zhongyuan Road within Hongcaoyuan, Hongcao Town, Shanwei Urban District
Factory Add:
West side of Centre Road and south side of Zhongyuan Road within Hongcaoyuan, Hongcao Town, Shanwei Urban District
Copyright© 2022 Guangdong Bao Jie Technology Co., Ltd.All Rights Reserved.


 EN
EN 





