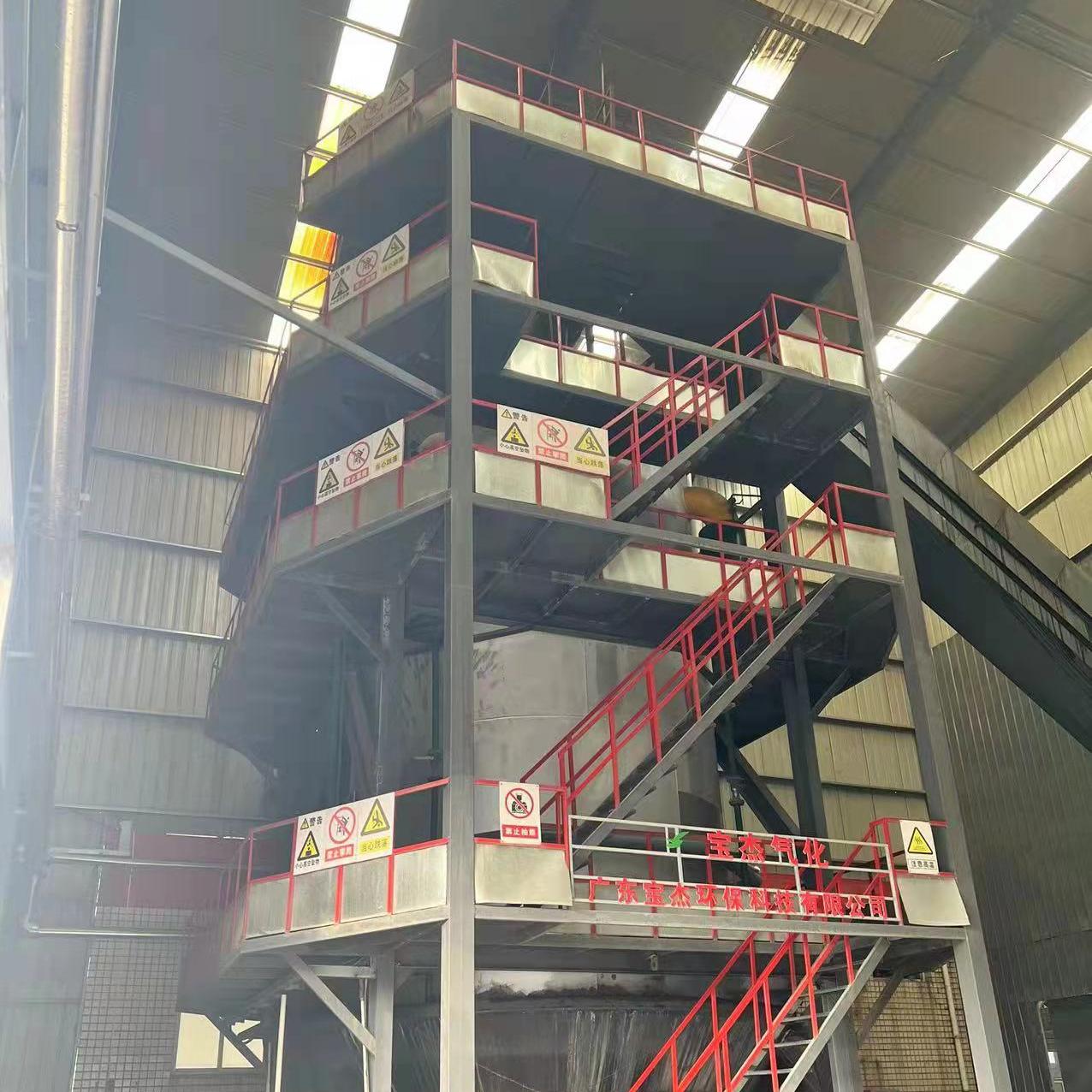
R&D and manufacture of biomass gasification equipment, environmental protection equipment, boiler equipment, investment in heating (steam) energy operation and management.
Tel:+86 0769-82928980
E-mail:[email protected]
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Industry News
Is Your Industry Ready to Turn Waste into Energy and Profit? The 20-Tonne Biomass Gasifier Explained
For energy-intensive industries, the rising cost of fossil fuels and increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices are two sides of the same coin. How do you maintain profitability while reducing your environmental footprint? The answer may lie not in looking forward, but in looking at your waste stream. What if the agricultural residue, wood chips, or other biomass waste your operation produces could become your most valuable source of clean, affordable energy? This is not a vision of the future; it’s the practical reality offered by a 20-tonne biomass gasification system. But what exactly is this technology, and how can it revolutionize your energy independence and bottom line?
What is a 20-Tonne Biomass Gasifier? The Engine of Circular Economics
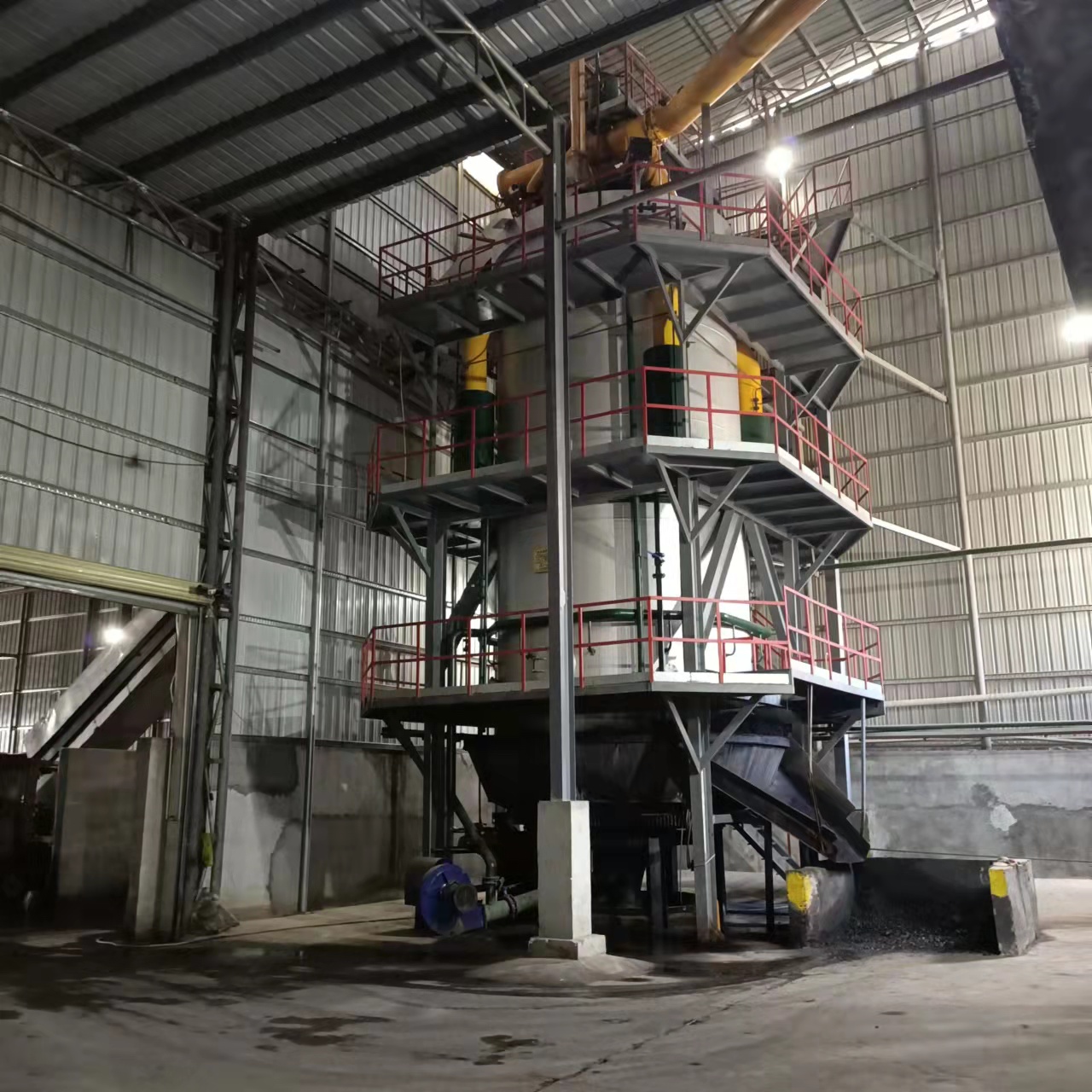
A 20-tonne biomass gasifier is a robust industrial-scale system designed to convert approximately 20 tonnes of biomass feedstock per day into a versatile combustible gas known as producer gas (syngas). This process, called gasification, involves heating the biomass in a controlled, high-temperature environment with a limited amount of oxygen. Instead of burning openly, the biomass breaks down molecularly, releasing a mixture of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane.
This “20-tonne” capacity is a significant sweet spot, making it ideal for medium-to-large industrial applications such as food processing plants, textile mills, ceramic and brick kilns, agricultural processing units, and small-scale power generation. It represents a system large enough to make a substantial impact on a factory’s energy needs without the colossal footprint and investment of a utility-scale plant.
From Waste to Watts: The Tangible Benefits of Adoption
Investing in a 20-tonne biomass gasifier is not just an environmental statement; it’s a strategic financial decision with a clear and compelling ROI.
- Drastic Reduction in Energy Costs: This is the most powerful motivator. By replacing expensive furnace oil, LPG, or natural gas with locally sourced, low-cost biomass, industries can slash their energy bills by 30% to 50% or more. The fuel source is often waste from your own operations or purchased from local agricultural networks, keeping energy spending within the local economy.
- Enhanced Energy Security and Price Stability: Are you tired of volatile global fossil fuel markets? Biomass prices are historically stable and predictable. By generating your own thermal energy on-site, you insulate your business from geopolitical shocks and supply chain disruptions, ensuring uninterrupted production.
- Carbon Neutrality and Environmental Compliance: The gasification process is considered carbon-neutral. The carbon dioxide released during combustion is roughly equal to what the biomass absorbed from the atmosphere during its growth. This significantly reduces your facility’s net greenhouse gas emissions, helping you meet CSR goals and comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. It also cleanly disposes of waste that might otherwise be openly burned, contributing to air pollution.
- Waste Valorization: This system transforms a liability—biomass waste that requires disposal—into a valuable asset. You are effectively creating energy from waste, turning a cost center into a profit center.

How It Works: A Glimpse into the Clean Energy Process
The journey from biomass to usable energy is a marvel of thermo-chemical engineering:
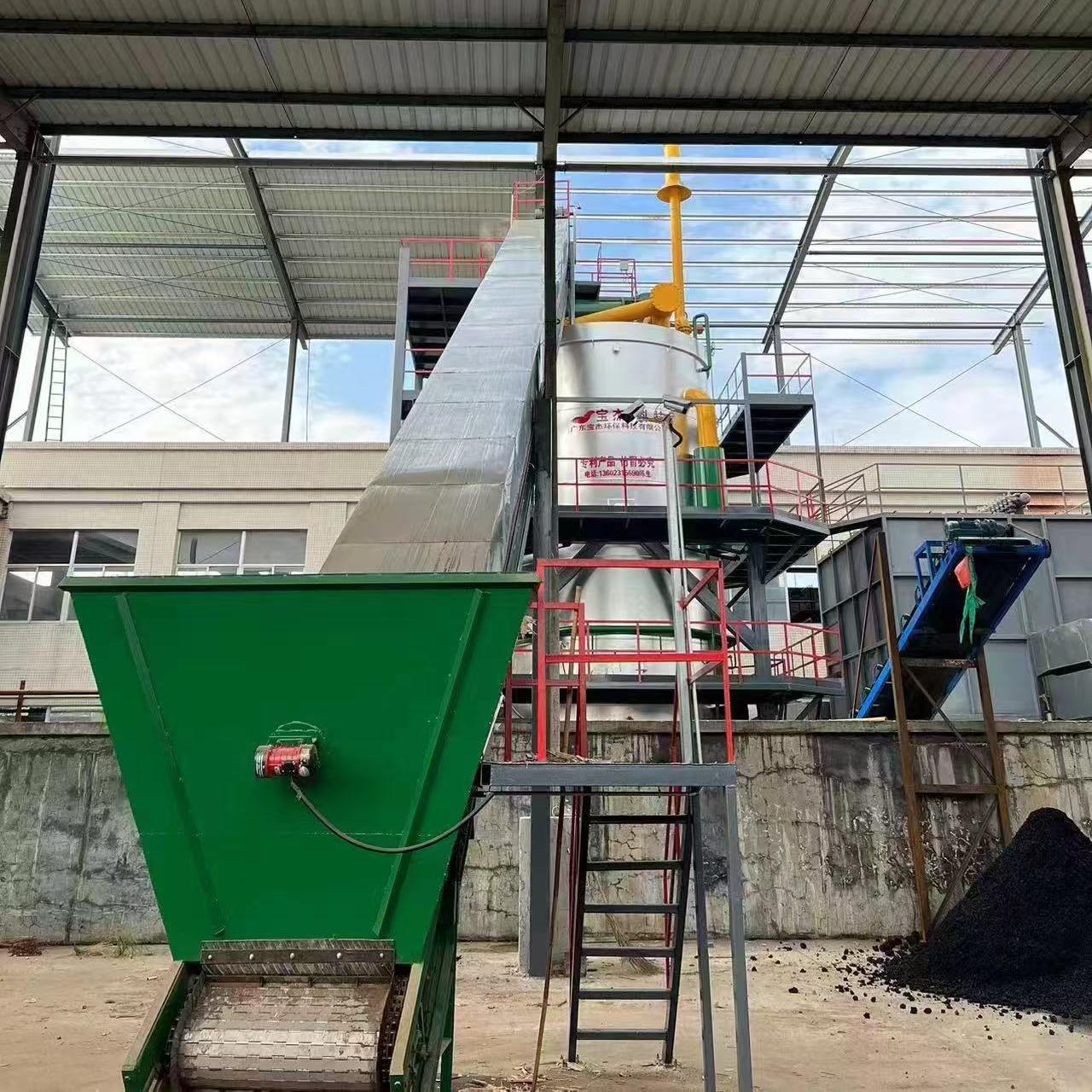
- Feedstock Preparation: Biomass (e.g., wood chips, rice husk, coconut shells, bagasse) is shredded and dried to achieve a uniform size and low moisture content, crucial for efficient gasification.
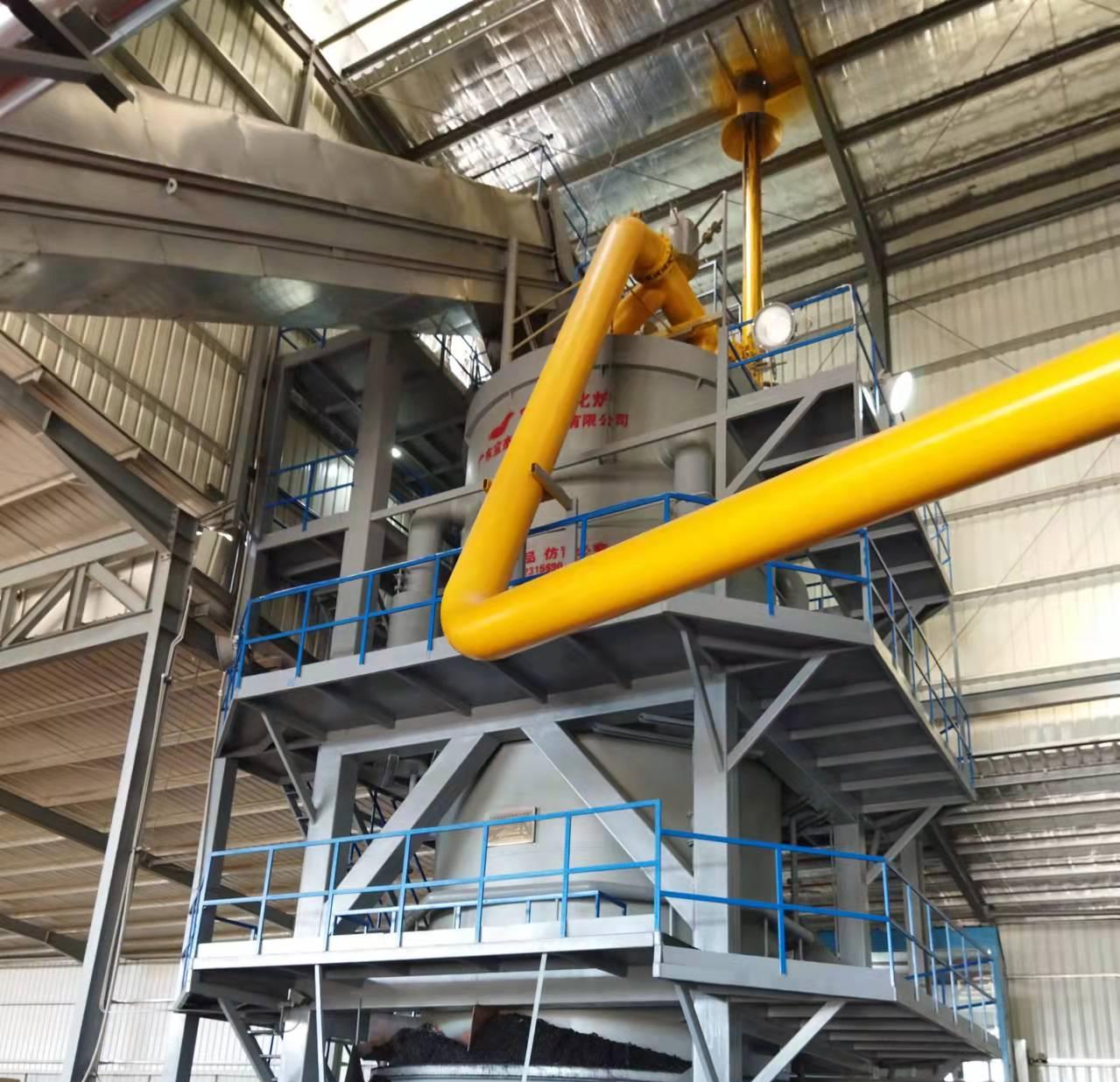
- Gasification: The prepared biomass is fed into the gasifier reactor. Through stages of drying, pyrolysis, oxidation, and reduction, the solid biomass is converted into raw producer gas and a small amount of biochar.
- Gas Cleaning: The hot, raw gas passes through a series of filters and coolers to remove particulate matter, tars, and other impurities, resulting in clean, cool syngas.
- Energy Application: The clean syngas is then piped directly to the application point. It can be combusted in:
- Thermal Applications: Custom-designed burners for boilers, furnaces, kilns, and dryers, providing precise high-temperature heat.
- Power Generation: As fuel for an internal combustion engine coupled to a generator to produce electricity.
Is a 20-Tonne System the Right Fit for Your Facility?
This solution is perfect for industries with a consistent thermal energy demand of 2-4 MWth or those looking to generate several hundred kW of power. The key to success is a reliable and sustainable supply of biomass feedstock within a reasonable distance to keep logistics costs low.
Quick Links
Products
contact Us
 Tel: +86 0769-82928980
Tel: +86 0769-82928980 Fax: [email protected]
Fax: [email protected] E-mail: [email protected]
E-mail: [email protected] Company Address: Dalang Chamber of Commerce Building, No. 288 Yinlang South Road, Dalang Town, Dongguan City 13333, China
Company Address: Dalang Chamber of Commerce Building, No. 288 Yinlang South Road, Dalang Town, Dongguan City 13333, China Factory Add:
West side of Centre Road and south side of Zhongyuan Road within Hongcaoyuan, Hongcao Town, Shanwei Urban District
Factory Add:
West side of Centre Road and south side of Zhongyuan Road within Hongcaoyuan, Hongcao Town, Shanwei Urban District
Copyright© 2022 Guangdong Bao Jie Technology Co., Ltd.All Rights Reserved.


 EN
EN 





